Overview
Hightouch optimizes syncs by sending only the rows that have changed since the last run.
This process is called change data capture (CDC), or diffing.
Without CDC, every sync would resend the entire dataset, causing unnecessary API calls, slower syncs, and wasted downstream processing.
How CDC works
Whenever a new sync is triggered, Hightouch compares the previous sync run to the current set of query results. To do this, Hightouch keeps a record of the data sent in the last sync. This record is the diff file.
CDC only considers mapped model columns when creating and updating the diff file. The only exception is custom destinations, such as the HTTP Request destination, which consider all columns.
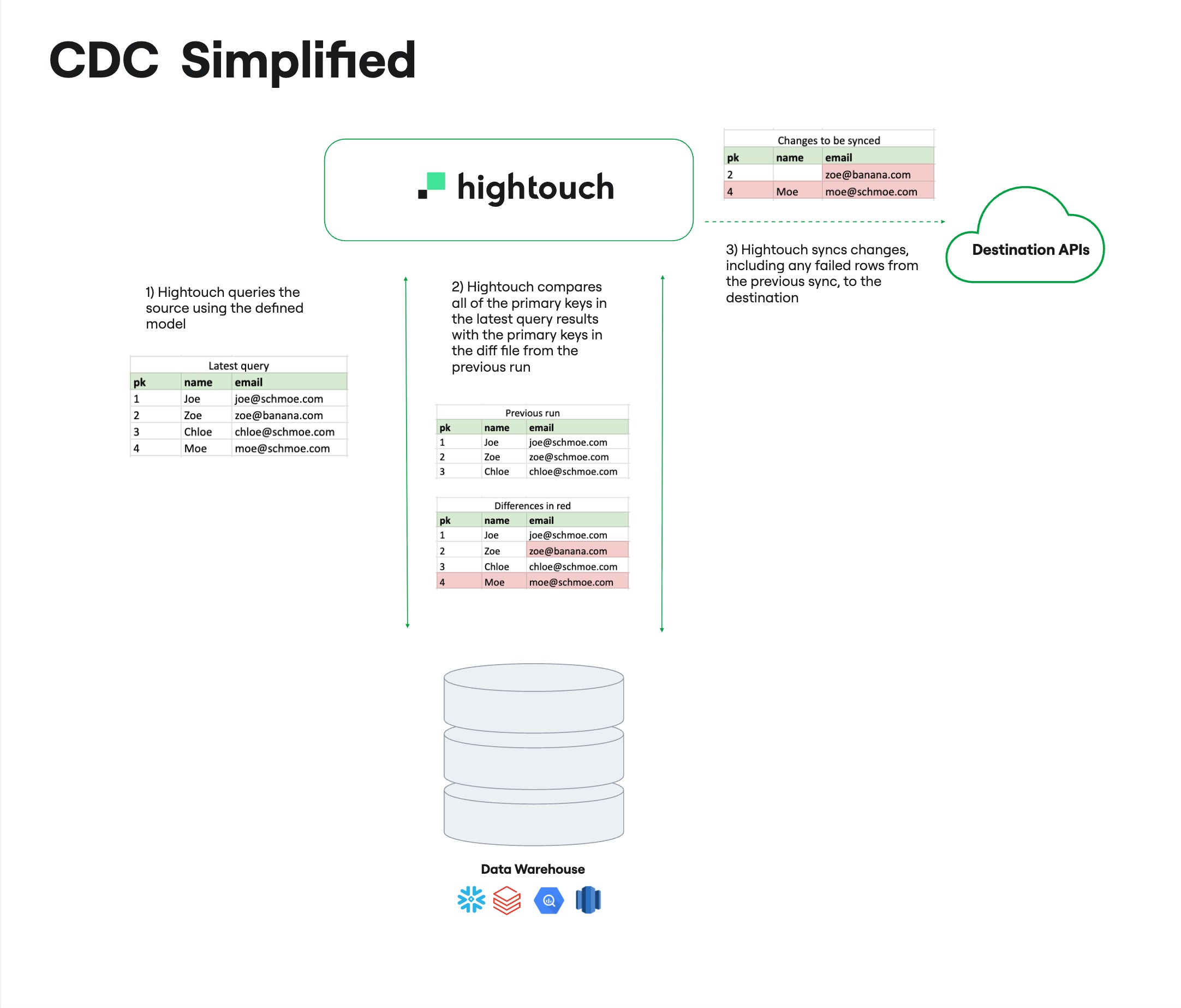
Steps in the CDC process:
- Hightouch queries the source using the defined model.
- Hightouch compares the current results to the results from the previous sync.
- Hightouch identifies differences by primary key:
- New rows
- Updated rows
- Removed rows
- Hightouch syncs only the changes to the destination, including any failed rows from the previous run.
- A new diff file is created for the next comparison.
Requirements
CDC relies on a unique primary key for every row in a model.
If primary keys are missing or duplicated, Hightouch can’t reliably track changes.
See Primary key requirements →.
CDC by sync mode
CDC behavior depends on the sync mode:
- Insert mode: only syncs rows whose primary key wasn’t present in the previous run.
- Update / Upsert modes: syncs rows where values have changed.
- All and Archive modes: do not perform CDC; every row is sent every run.
Difference-based CDC
Hightouch uses a method called difference-based CDC because it compares the full before/after query results.
This is required when syncing from warehouses, since they cannot produce CDC logs for arbitrary SQL queries or dbt models.
In contrast, OLTP databases (like Postgres or MySQL) log incremental changes natively, which ETL tools often use when sending data into warehouses.
Because Hightouch does the reverse (sending data from warehouses), log-based CDC isn’t possible. This is a key distinction between ETL and reverse ETL.
When CDC occurs
CDC happens after Hightouch receives the query results from the source and before data is written to the destination.
If you see the sync status Querying in the UI, Hightouch is in one of these states:
- Waiting for query results
- Saving the diff file
- Performing CDC computation
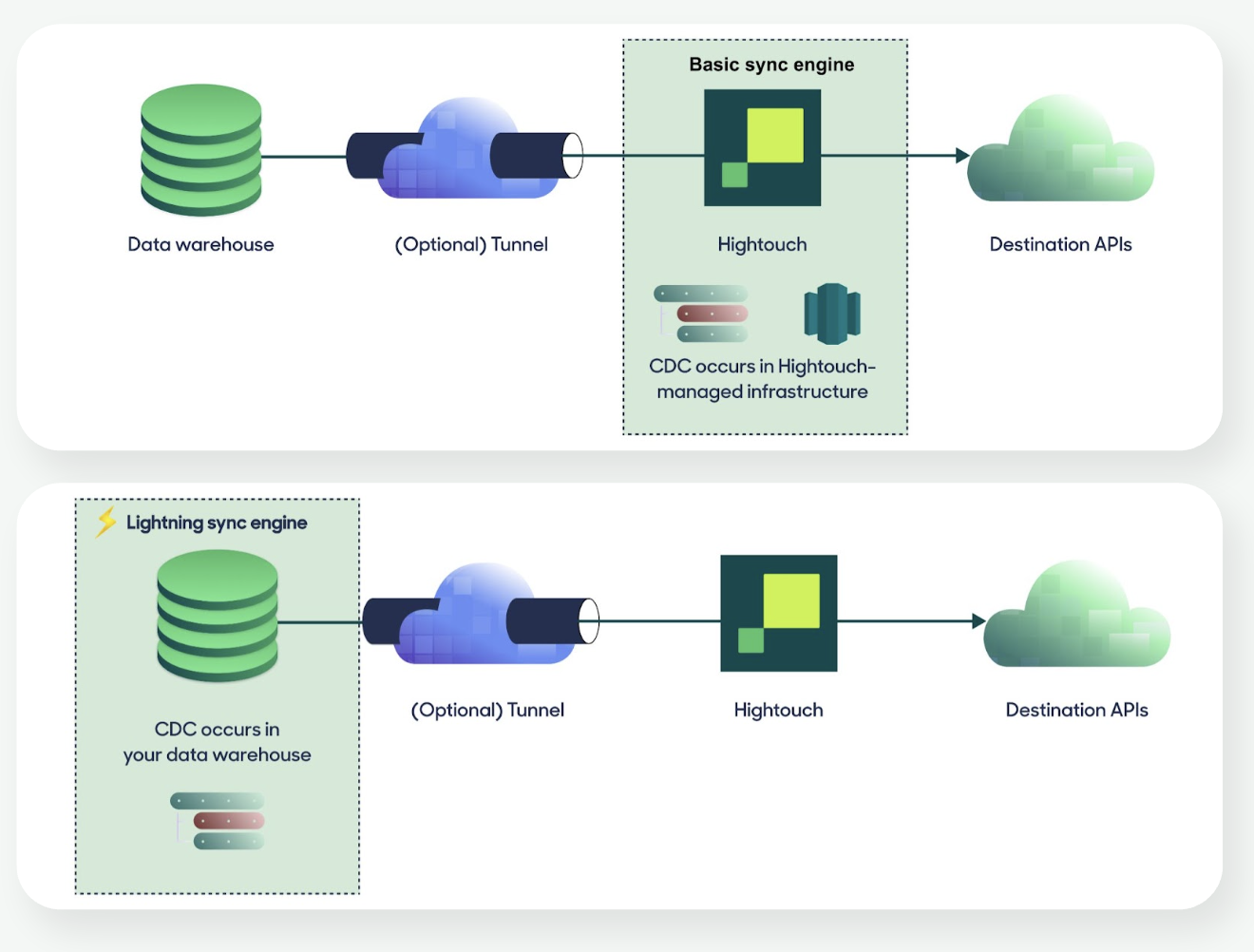
Where CDC is computed
By default, CDC is performed on Hightouch-managed infrastructure.
For supported sources, you can enable the Lightning Sync Engine to compute CDC directly in your warehouse.
- Basic engine: CDC runs on Hightouch infra.
- Lightning engine: CDC runs in your warehouse, enabling faster syncs at higher volumes.
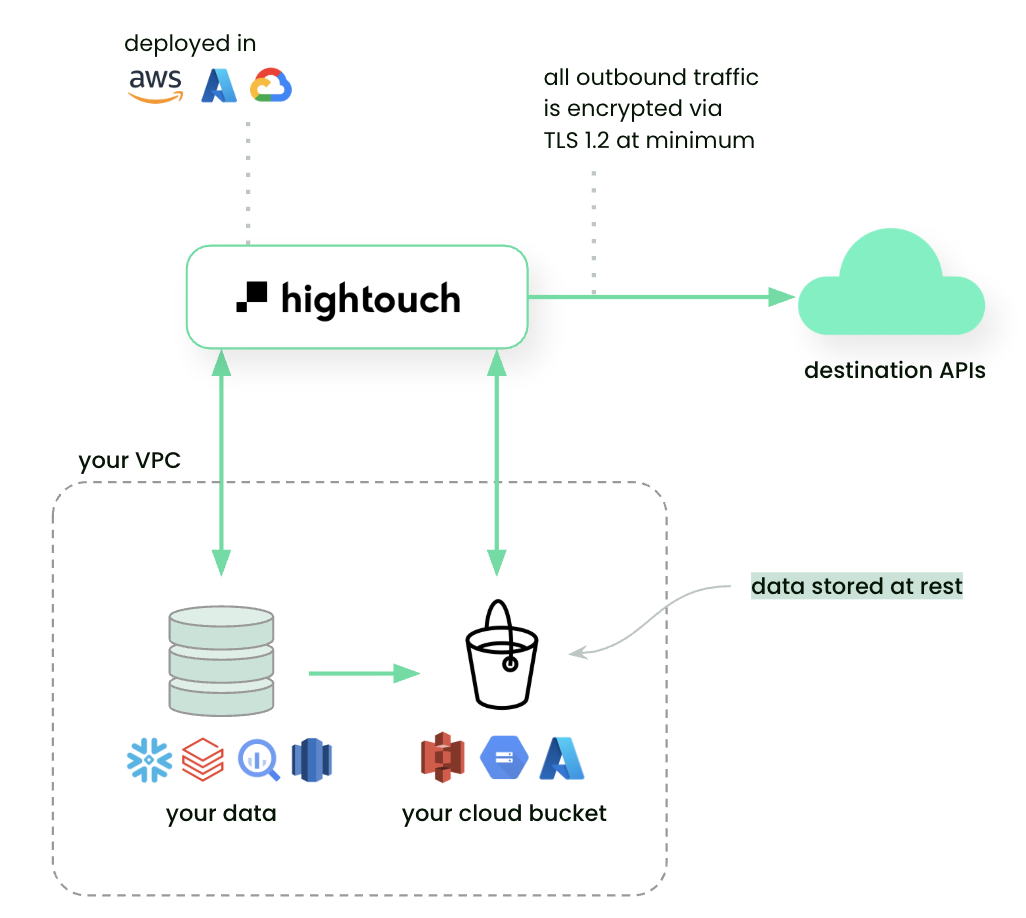
Where CDC data is stored
Hightouch stores previous query results (diff files) to compute changes.
- By default, diff files are stored in an encrypted Hightouch-managed bucket.
- Some plans allow you to bring your own bucket → to store diffs in your own infrastructure.
Diff files are retained for 30 days in Hightouch-managed storage.
If a sync doesn’t run for more than 30 days, you’ll need to reset CDC or run a full resync.
Resetting or resyncing CDC
Sometimes you may need to reset how CDC tracks changes. Common cases:
- Primary key changes: Hightouch prompts you to reset CDC when you change a model’s primary key.
- Resync full query: forces Hightouch to resend all rows, then resume CDC tracking.
- Reset CDC: ignores existing state and starts fresh on the next run (no data is sent during the reset run).
FAQ
What happens if I change my model configuration?
- Only mapped columns affect CDC tracking, except for HTTP Request destinations, which consider all columns.
- If you change a column’s primary key, Hightouch requires a CDC reset.
- For other model changes, see Model configuration docs.
As explained in the primary key updates section, if you alter a model's primary key by selecting a different column, you will be prompted to reset the change data capture for all syncs that depend on that model. Be careful when modifying primary keys. If you keep the same column name but alter the way its values are calculated, some records may be added or deleted in your destination, depending on how your sync is configured.
Learn more about changes to your model configuration in the model column changes section.
Does Hightouch keep historical CDC files?
No. Only the most recent diff file is stored and compared against.
What happens if my sync fails?
CDC re-attempts failed rows on the next run.
What happens if I stop syncing for more than 30 days?
Diff files in managed storage expire after 30 days. You’ll need to reset CDC or perform a full resync.
What happens if I change sync mappings?
Changing mappings may cause a full reprocess. See Field mapping updates.