Databricks is a data science and analytics platform built on top of Apache Spark. Databricks implement the Data Lakehouse concept in a single unified, cloud based platform.
Overview
Databricks is a popular source that supports our Reverse ETL, Composable CDP, and AI Decisioning features. This article discusses the steps for connecting to Databricks.
You can connect Databricks to Hightouch using Databricks Partner Connect to bypass the setup steps outlined below. You can learn more about this in Databricks' documentation.
You may need to allowlist Hightouch's IP addresses to let our systems connect to your Databricks warehouse. Reference our networking docs to determine which IP addresses you need to allowlist.
You can also securely connect to your Databricks warehouse using AWS PrivateLink. AWS PrivateLink is a Business Tier feature.
Databricks credential setup
Hightouch allows you to authenticate with Databricks using one of two methods: Either OAuth or a Personal Access Token (PAT).
We recommend using OAuth for configuring new connections.
Configuring a service principal with OAuth
-
Create a service principal.
-
In your Databricks workspace, go to the user dropdown at the top right and select Settings.
-
In the Identity and access page, find Service Principals and click Manage.
-
Choose Add new, give your service principal a name, and click Add.
-
Take note of the Service Principal name as well as the Application id listed on the Service Principal Configurations page. This is a UUID (for example,
63fc7e90-a8a2-4639-afd8-36ef6bb67cfa). You may need this later to complete setup.
-
-
Create an OAuth secret pair.
-
On the page for the Service Principal created above, to go the Secrets tab.
-
Click Generate secret. A dialog will pop up with a Secret and a Client ID. Take careful note of these values as it is only visible now; you can't look it up later.
-
-
Grant the necessary catalog permissions to your new Service Principal. The above steps are sufficient to connect and authenticate, but the Service Principal may not be authorized to execute queries against your Databricks catalog. Depending on your Databricks workspace configuration, it may already be configured with the necessary permissions; but if the connection test fails, you may need to follow these steps.
-
In the Databricks sidebar on the left, click Catalog and locate your schema in the tree view.
-
Select the schema and open the Permissions page. Click the Grant button.
-
In the Principals input box, type the name of your new Service Principal.
-
If you are using the Lightning sync engine (recommended; see below), select the Data Editor preset or manually grant the following permissions:
USE SCHEMAEXECUTEREAD VOLUMESELECTMODIFYCREATE TABLE- Make sure to enable the checkbox at the bottom to "Also grant
USE CATALOG"
-
If you are using the Basic sync engine, select the Data Reader preset or manually grant the following permissions:
USE SCHEMAEXECUTEREAD VOLUMESELECT- Make sure to enable the checkbox at the bottom to "Also grant
USE CATALOG"
-
-
-
You may also need to configure warehouse permissions. As with the previous step concerning catalog permissions, your Databricks workspace configuration may or may not automatically grant the Service Principal permission to use the compute resources. You can read more about it in the Databricks docs.
-
In the Databricks sidebar, click Compute and find your data warehouse. It may be located on the SQL warehouses page.
-
On the far right column of the row corresponding to the desired warehouse, click the icon for the kebab menu ⋮, then Permissions.
If you do not see the Permissions option, you may lack the privileges necessary to configure permissions—even if you are a Databricks workspace admin. If this happens, please contact your Databricks account admin.
-
Enter the name of your Service Principal and ensure that the setting in the dropdown is set to Can use. Click Add.
-
Alternative: Configuring a Personal Access Token (PAT)
-
In your Databricks Account console, go the Workspaces page. Select the relevant workspace and then click Open workspace.
-
In your workspace, go the Compute page and click the relevant cluster. This brings you to its Configuration tab.
-
At the bottom of the page, expand the Advanced Options toggle and open the JDBC/ODBC tab.
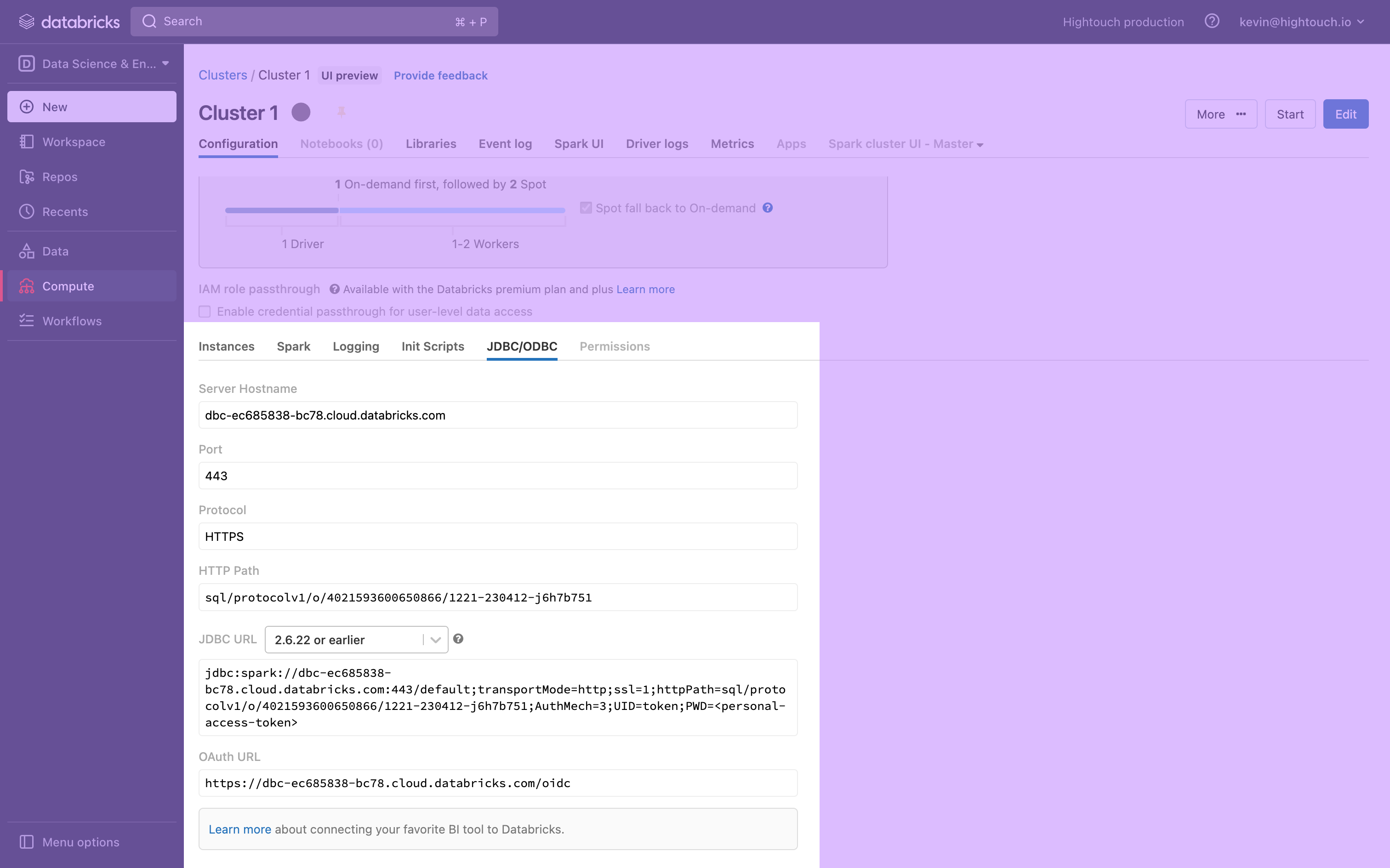
-
This tab displays your cluster's Server Hostname, Port, and HTTP Path, which you need to connect to Hightouch. Keep the tab open, or save these to a secure location.
-
Create a Personal access token by following the Databricks documentation.
Once you've saved these Databricks credentials, you're ready to set up the connection in Hightouch.
Connection configuration
To get started, go to the Sources overview page and click the Add source button. Select Databricks and follow the steps below.
Configure your source
Enter the following required fields into Hightouch:
-
Server hostname: To find your server hostname, visit the Databricks web console and locate your cluster. Then, click to reveal Advanced options and navigate to the JDBC/ODBC tab.
-
Port: The default port number is 443, but yours may be different. To find your port, visit the Databricks web console and locate your cluster. Then, click to reveal Advanced options and navigate to the JDBC/ODBC tab.
-
HTTP path: To find your HTTP path, visit the Databricks web console and locate your cluster. Then, click to reveal Advanced options and navigate to the JDBC/ODBC tab.
You can choose to route all queries to a single HTTP path, or configure separate HTTP paths optimized for different workloads (recommended):
-
Route all queries to a single HTTP path: Use this option if you want to use a single HTTP path for all Hightouch operations.
-
Route queries to different HTTP paths (split by workload) (Recommended): This option allows you to optimize performance by routing different types of queries to different HTTP paths:
- Batch HTTP path: For background jobs like sync runs, schema sampling, audience snapshots, and other workloads that are not latency-sensitive.
- Interactive HTTP path: For latency-sensitive queries (e.g., audience previews) and heavier workloads that need more compute (e.g., identity resolution).
-
-
(Optional) Catalog: You can optionally include a Databricks catalog. Catalogs are the first level of Unity Catalog's three-level namespace. If Lightning engine is enabled, the 'hightouch_audit' and 'hightouch_planner' schemas need to be created in the catalog specified here. If this field is left empty, these schemas should be created in the default catalog. Note that data in other catalogs can still be accessed for model creation by specifying the full name (catalog.schema.table) in the Hightouch SQL interface.
-
Schema: The initial schema to use for the connection.
-
SQL dialect: By default, Hightouch assumes that your queries use the Databricks SQL dialect. You may wish to override this behavior if your queries use legacy ANSI SQL-92 syntax. Some features are not available when legacy syntax is used.
Choose your sync engine
For optimal performance, Hightouch tracks incremental changes in your data model—such as added, changed, or removed rows—and only syncs those records. You can choose between two different sync engines for this work.
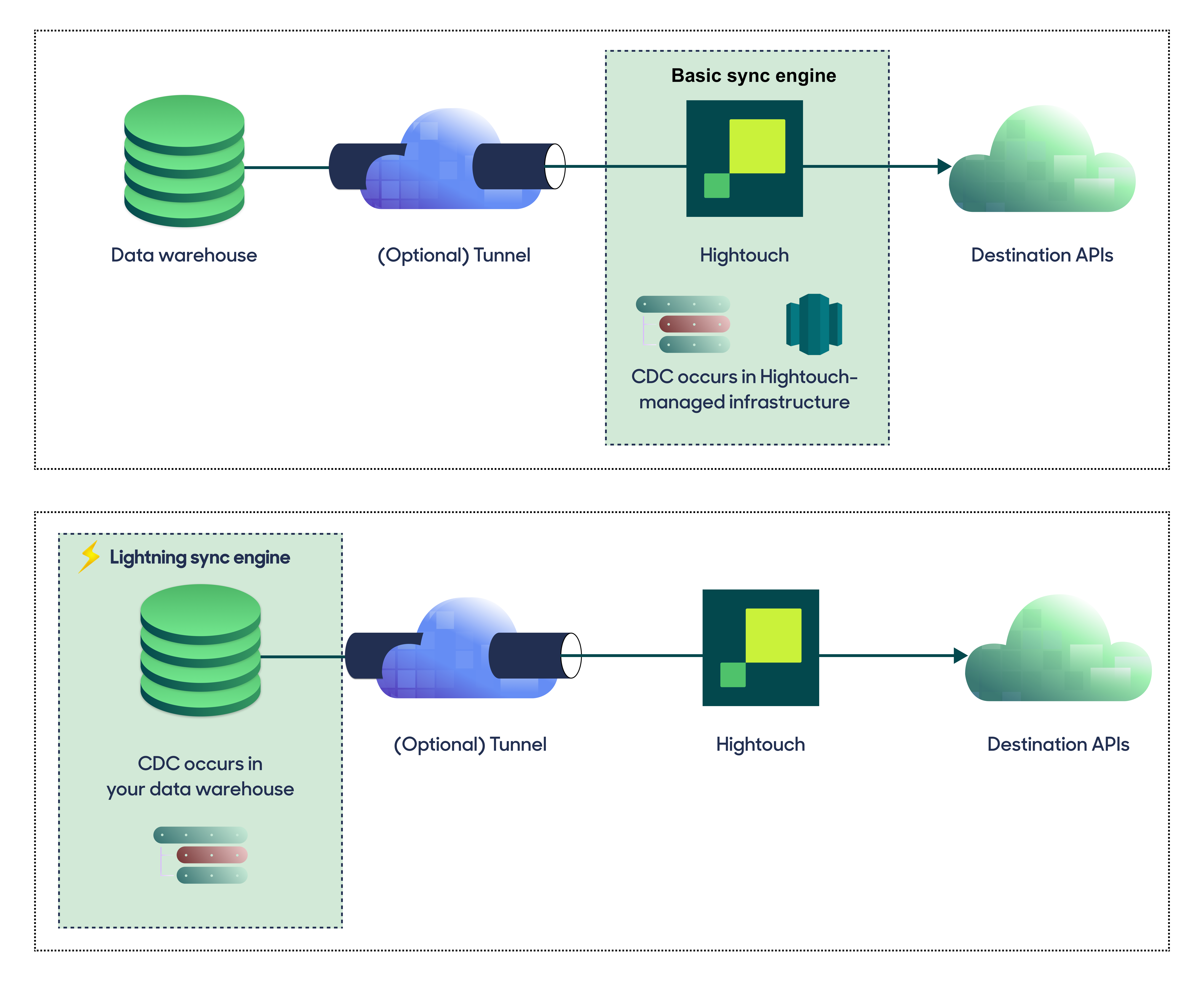
The Basic engine requires read-only access to Databricks. Hightouch executes a query in your database, reads all query results, and then determines incremental changes using Hightouch's infrastructure. This engine is easier to set up since it requires read—not write—access to Databricks.
The Lightning engine requires read and write access to Databricks. The engine stores previously synced data in a separate schema in Databricks managed by Hightouch. In other words, the engine uses Databricks to track incremental changes to your data rather than performing these calculations in Hightouch. Therefore, these computations are completed more quickly.
If you select the Basic engine, you can switch to the Lightning engine later. Once you've configured the Lightning engine, you can't move back to the Basic engine without recreating Databricks as a source.
To learn more, including migration steps and tips, check out the Lightning sync engine docs.
Basic versus Lightning engine comparison
The Lightning sync engine requires granting write access to your data warehouse, which makes its setup more involved than the Basic sync engine. However, it is more performant and reliable than the Basic engine. This makes it the ideal choice to guarantee faster syncs, especially with large data models. It also supports more features, such as Warehouse Sync Logs, Match Booster, and Identity Resolution.
| Criteria | Basic sync engine | Lightning sync engine |
|---|---|---|
| Performance | Slower | Quicker |
| Ideal for large data models (over 100 thousand rows) | No | Yes |
| Reliability | Normal | High |
| Resilience to sync interruptions | Normal | High |
| Extra features | None | Warehouse Sync Logs, Match Booster, Identity Resolution |
| Ease of setup | Simpler | More involved |
| Location of change data capture | Hightouch infrastructure | Databricks schemas managed by Hightouch |
| Required permissions in Databricks | Read-only | Read and write |
| Ability to switch | You can move to the Lightning engine at any time | You can't move to the Basic engine once Lightning is configured |
Lightning engine setup
To set up the Lightning engine, ensure that your Databricks user or service principal has the appropriate permissions. You can do so by running the following SQL snippet.
Before running the snippet, make sure to include your own username, which can be found in the top right corner of the Databricks web console. Alternatively, you can create an API-only service principal by following these instructions.
CREATE SCHEMA IF NOT EXISTS hightouch_audit;
CREATE SCHEMA IF NOT EXISTS hightouch_planner;
GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON SCHEMA hightouch_audit TO <YOUR_USER>;
GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON SCHEMA hightouch_planner TO <YOUR_USER>;
The hightouch_audit and hightouch_planner schemas exist to keep Hightouch's temporary tables, logs, and other
artifacts separate from your source data. This simplifies governance because you can restrict write access to only
these Hightouch-managed schemas. We recommend using GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES for simplicity, but you can also grant the
required privileges separately to achieve the same effect.
(“Temporary tables” here refers to tables that Hightouch will automatically clean up once they are no longer
needed; it doesn't necessarily refer to special table types in the warehouse.)
If you are using a Service Principal to connect, you may need to specify the user
above by UUID rather than name. For example, if you have created a Service Principal
named test_principal with an Application Id of 63fc7e90-a8a2-4639-afd8-36ef6bb67cfa,
you may need to run
GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON SCHEMA hightouch_audit TO 63fc7e90-a8a2-4639-afd8-36ef6bb67cfa;
Provide credentials
Enter the Access token you generated in the Databricks credential setup.
Test your connection
When setting up a source for the first time, Hightouch validates the following:
- Network connectivity
- Databricks credentials
- Permission to list schemas and tables
- Permission to write to
hightouch_plannerschema - Permission to write to
hightouch_auditschema
All configurations must pass the first three, while those with the Lightning engine must pass all of them.
Some sources may initially fail connection tests due to timeouts. Once a connection is established, subsequent API requests should happen more quickly, so it's best to retry tests if they first fail. You can do this by clicking Test again.
If you've retried the tests and verified your credentials are correct but the tests are still failing, don't hesitate to .
Next steps
Once your source configuration has passed the necessary validation, your source setup is complete. Next, you can set up models to define which data you want to pull from Databricks.
The Databricks source supports these modeling methods:
- writing a query in the SQL editor
- using the visual table selector
- leveraging existing dbt models
- leveraging existing Sigma workbooks
The SQL editor allows you to query data from all databases that your Databricks credentials have access to, unless you specify a catalog. The table selector only supports querying from the schema specified in the source configuration.
You may also want to consider storing sync logs in Databricks. Like using the Lightning sync engine versus the standard one, this feature lets you use Databricks instead of Hightouch infrastructure. Rather than performance gains, it makes your sync log data available for more complex analysis. Refer to the warehouse sync logs docs to learn more.
You must enable the Lightning sync engine to store sync logs in your warehouse.
Tips and troubleshooting
If you encounter an error or question not listed below and need assistance, don't hesitate to . We're here to help.
Unity Catalog support
Hightouch integrates with Databricks' Unity Catalog feature. During initial configuration, just make sure to include a catalog.
Subquery error
Some Databricks models return the following error:
java.lang.IllegalArgumentException: requirement failed: Subquery subquery#485, [id=#937] has not finished {...}.
This error can occur when the model query contains a subquery, especially when the subquery has an ORDER BY clause.
For example:
SELECT user_query.*
FROM (
SELECT * FROM default.subscriptions_table
ORDER BY last_name
) user_query.*
The best way to resolve the error is to rewrite your model query to remove subqueries. Common table expressions (CTE) are supported. If you require assistance, don't hesitate to .
Error connecting to the database. Unauthorized/Forbidden: 403
This error can occur when testing the source connection or when running a sync that uses a Databricks model. It is typically caused by an expired Databricks access token. To solve this, generate a new token and insert it in the source configuration.
