Connect to your internal microservices via a message queue
Overview
Hightouch integrates with RabbitMQ so you can send data from your warehouse as messages to a RabbitMQ broker without writing and maintaining code, letting you build a custom connector to your internal systems.
Hightouch supports all managed RabbitMQ brokers (Amazon MQ, CloudAMQP, etc.) and can also connect to self-hosted instances.
Getting started
Connect to your RabbitMQ server
For Hightouch to connect to your RabbitMQ server, you need to enter the connection parameters of your RabbitMQ URI. These parameters include the protocol used, server connection details (host address and port), authentication credentials (username and password) and vhost. You also need to enter your Management Portal URL for Hightouch to query the queues in your RabbitMQ server,.
- Protocol: Select the protocol used for your RabbitMQ server. This is either
amqporamqps. - Host: Enter your host address to establish the underlying TCP/IP connection to the server.
- Port: Enter your port number to establish the underlying TCP/IP connection to the server.
- VHost: Enter you vhost. The default value is
/. - Management Portal: Enter your management portal URL. This can usually be found on the details page for your hosted RabbitMQ solution.
- Username and Password: Enter your RabbitMQ server username and password.
Syncing data
Once you've connected your RabbitMQ server to Hightouch, you can configure a sync that send messages whenever rows are added, changed, or removed in your model.
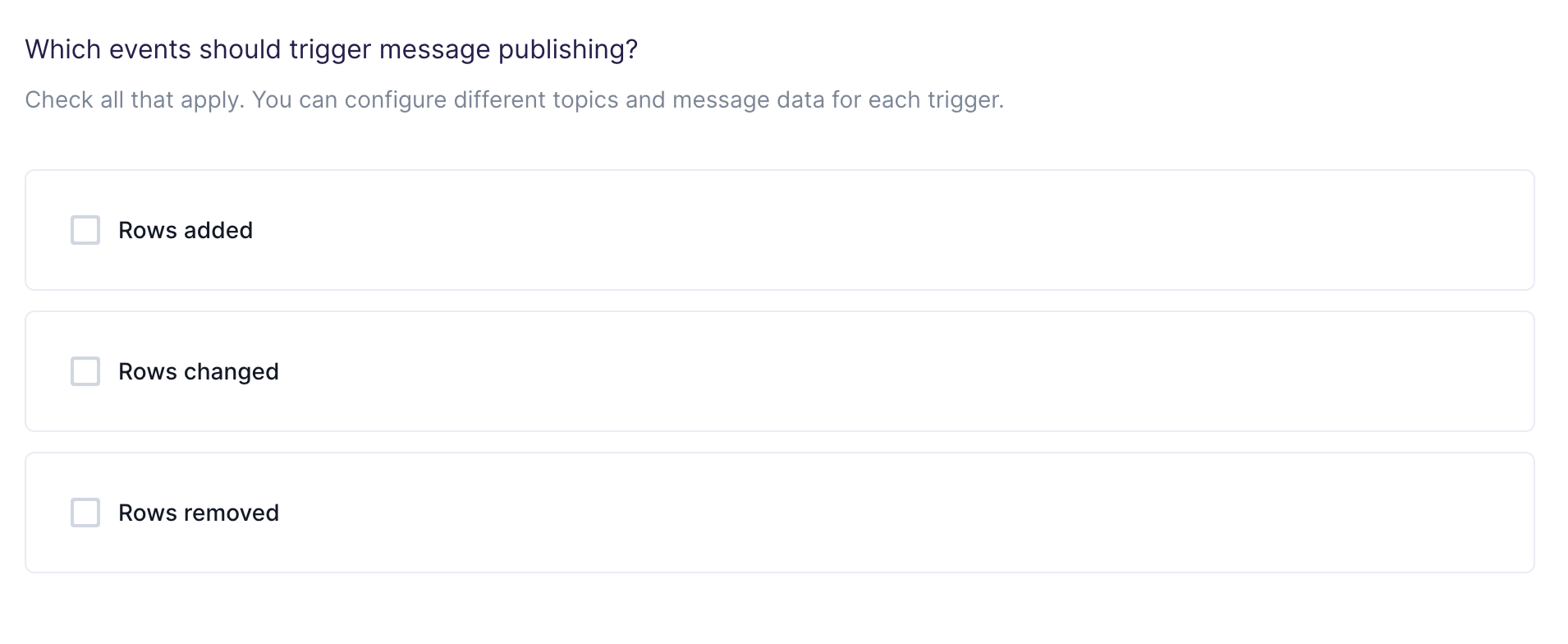
Configure your events trigger
Hightouch monitors your data model for added, changed, and removed rows. In this step, you specify which of these events should trigger message publishing.
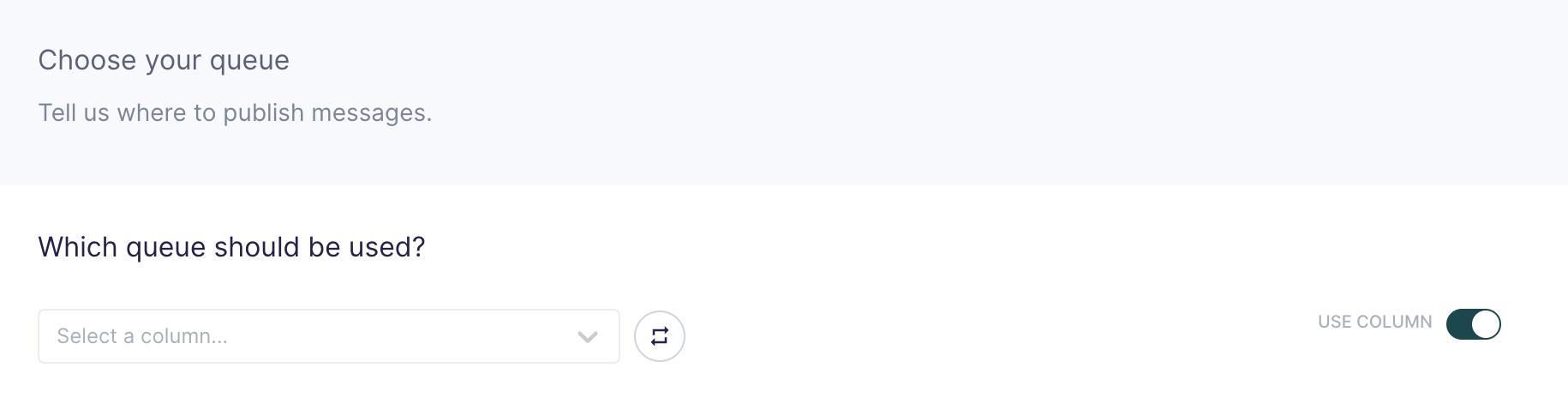
Choose your queue
In this step, you choose which queues to publish the messages to. Hightouch allows you to sync to existing queues that are already in your RabbitMQ.
Suppose you want to sync to multiple existing queues but don't want to create a new sync for every queue. As long as your model has a column associated to queue names in your RabbitMQ server, Hightouch can sync to multiple RabbitMQ queues in just one sync. To enable this feature, toggle USE COLUMN, and select a column in your model containing the queue name rows.
When syncing to multiple queues, if a queue name in the selected column of your model doesn't exist in RabbitMQ, then the sync for that message will fail.
Customize your message
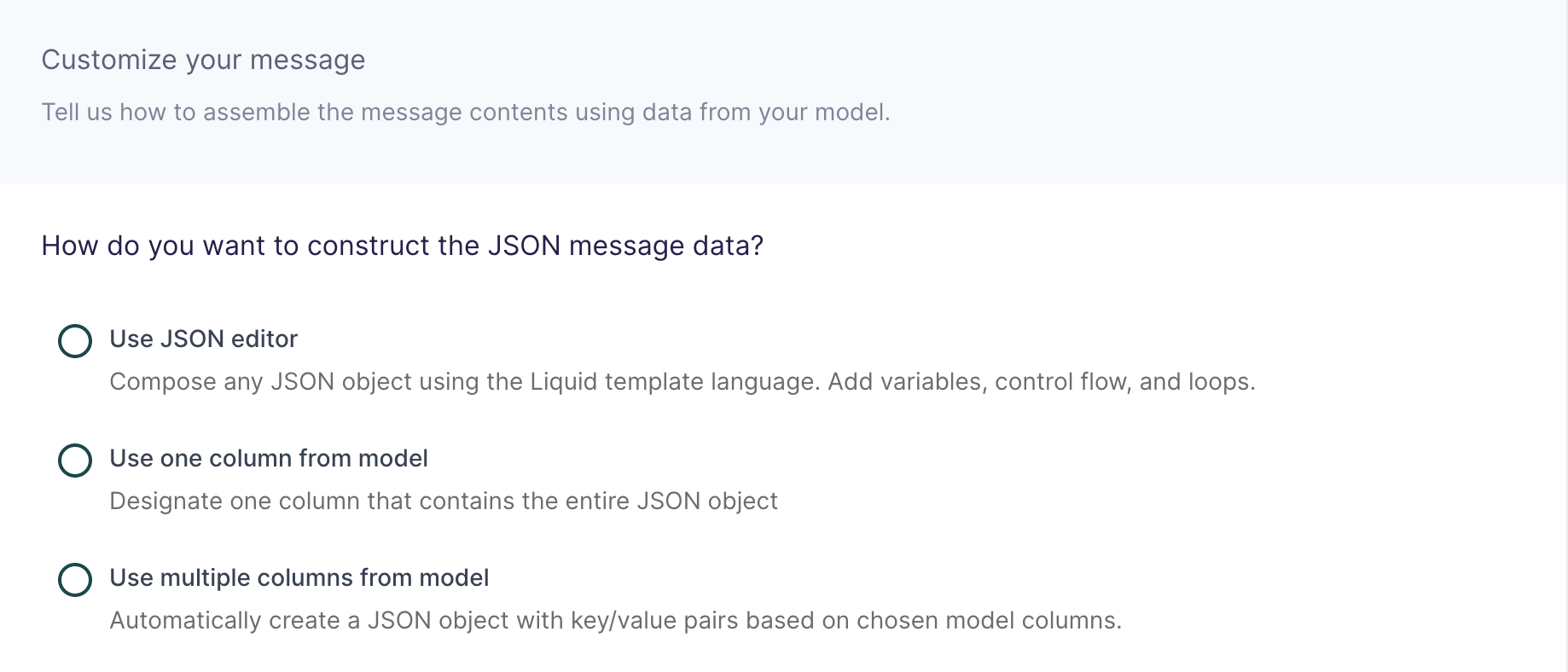
In this step, you tell Hightouch how to build the JSON message data object using data from your model.
This destination offers three methods of composing a JSON object:
Use JSON editor
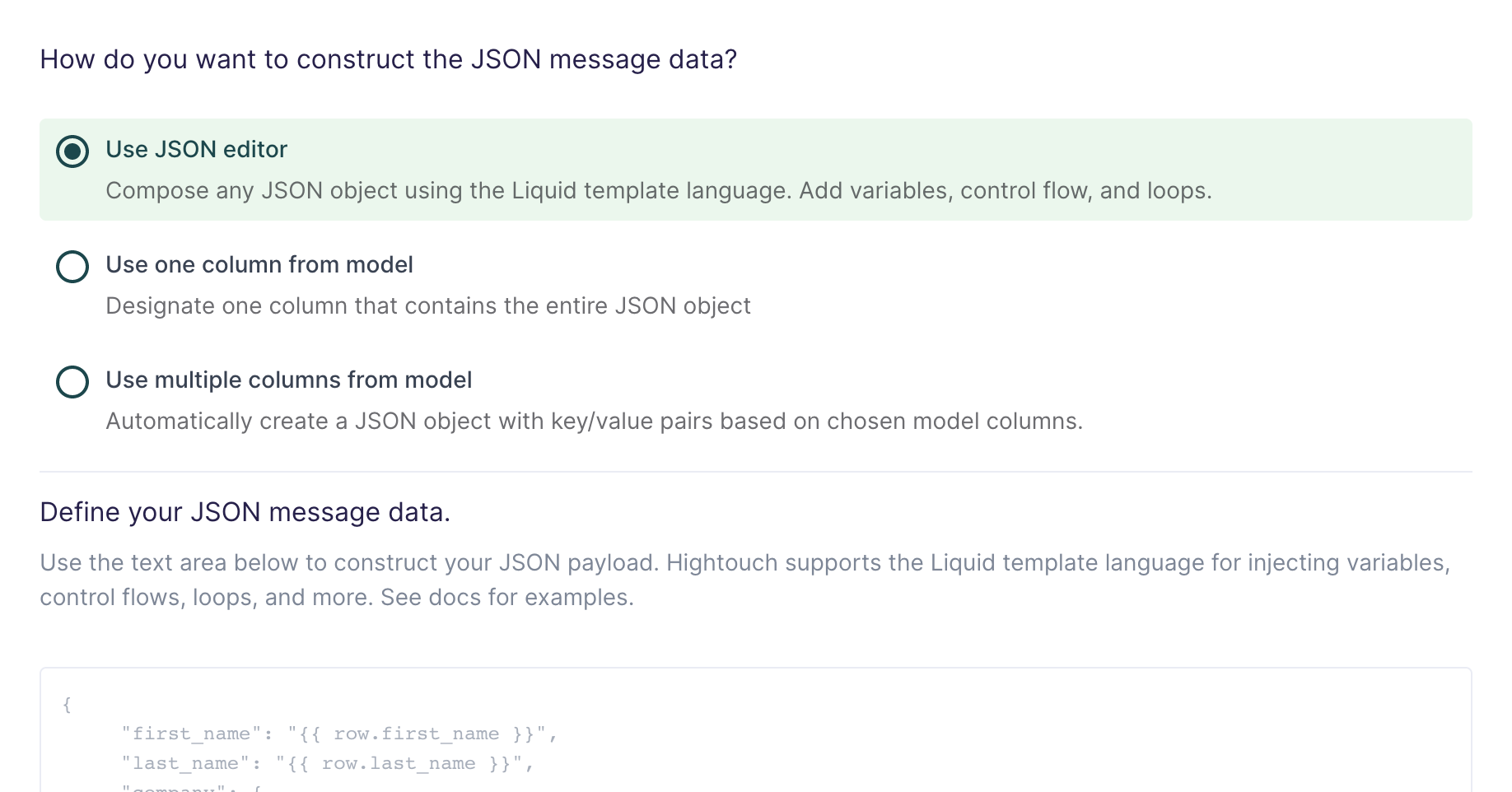
With the JSON editor, you can compose any JSON object using the Liquid template language. This is particularly useful for complex message data bodies containing nested objects and arrays, which can sometimes be difficult to model entirely in SQL.
Suppose your data model looks like this:
| full_name | age | email_address | phone_number |
|---|---|---|---|
| John Doe | 30 | john@example.com | +14158675309 |
And you want your message data like this:
{
"name": "John Doe",
"age": 30,
"contact_info": [
{
"type": "email",
"value": "john@example.com"
},
{
"type": "phone",
"value": "+14158675309"
}
]
}
Your Liquid template should look like this:
{
"name": "{{row.full_name}}",
"age": {{row.age}},
"contact_info": [
{
"type": "email",
"value": "{{row.email_address}}"
},
{
"type": "phone",
"value": "{{row.phone_number}}"
}
]
}
This makes it so you can reference any column using the syntax {{row.column_name}}. You can also use advanced Liquid features to incorporate control flow and loops into your dynamic message data.
When injecting strings into your JSON object, be sure to surround the Liquid tag in double quotes.
Use one column from model
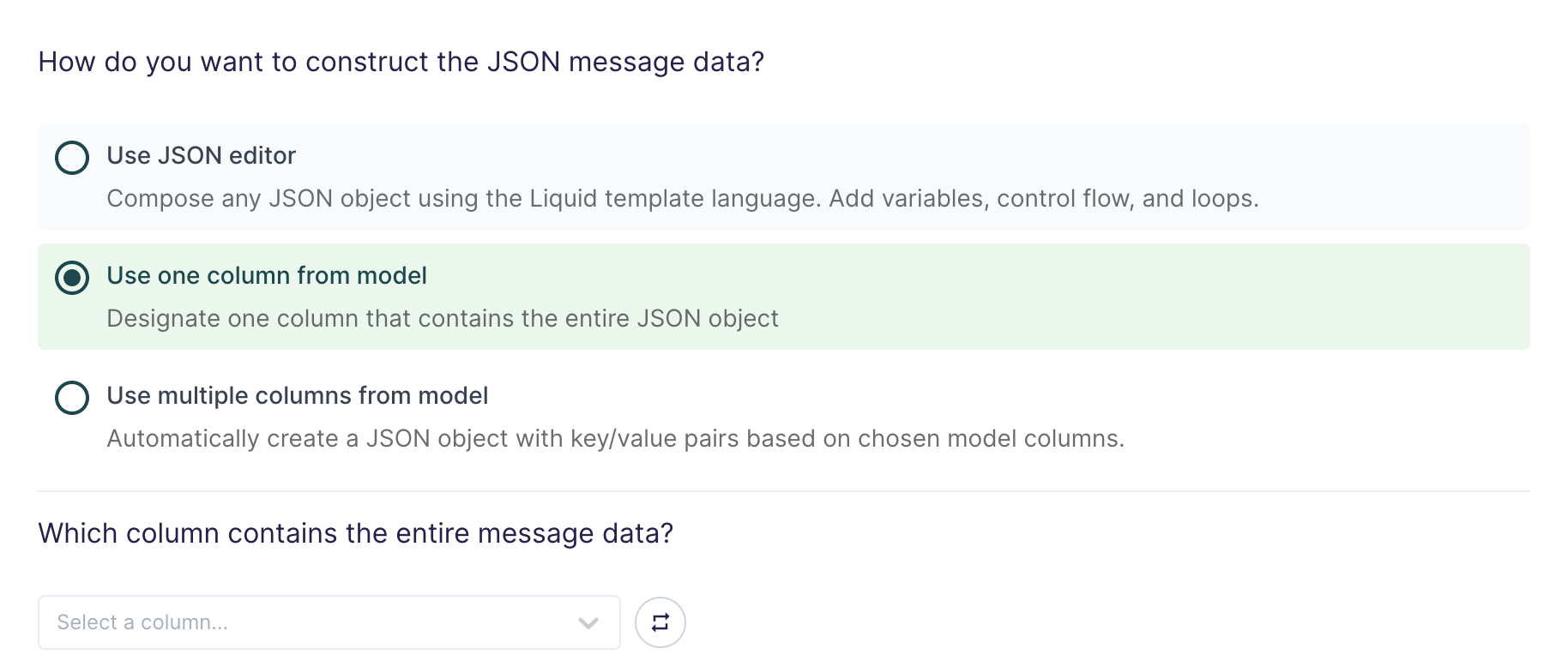
If you're already storing JSON data in your source, or if you have the ability to construct a JSON object using SQL, you can select one column in your model that already contains the full message data.
This setting is commonly used when syncing web events that have already been collected and stored as JSON objects in your database.
Use multiple columns from model
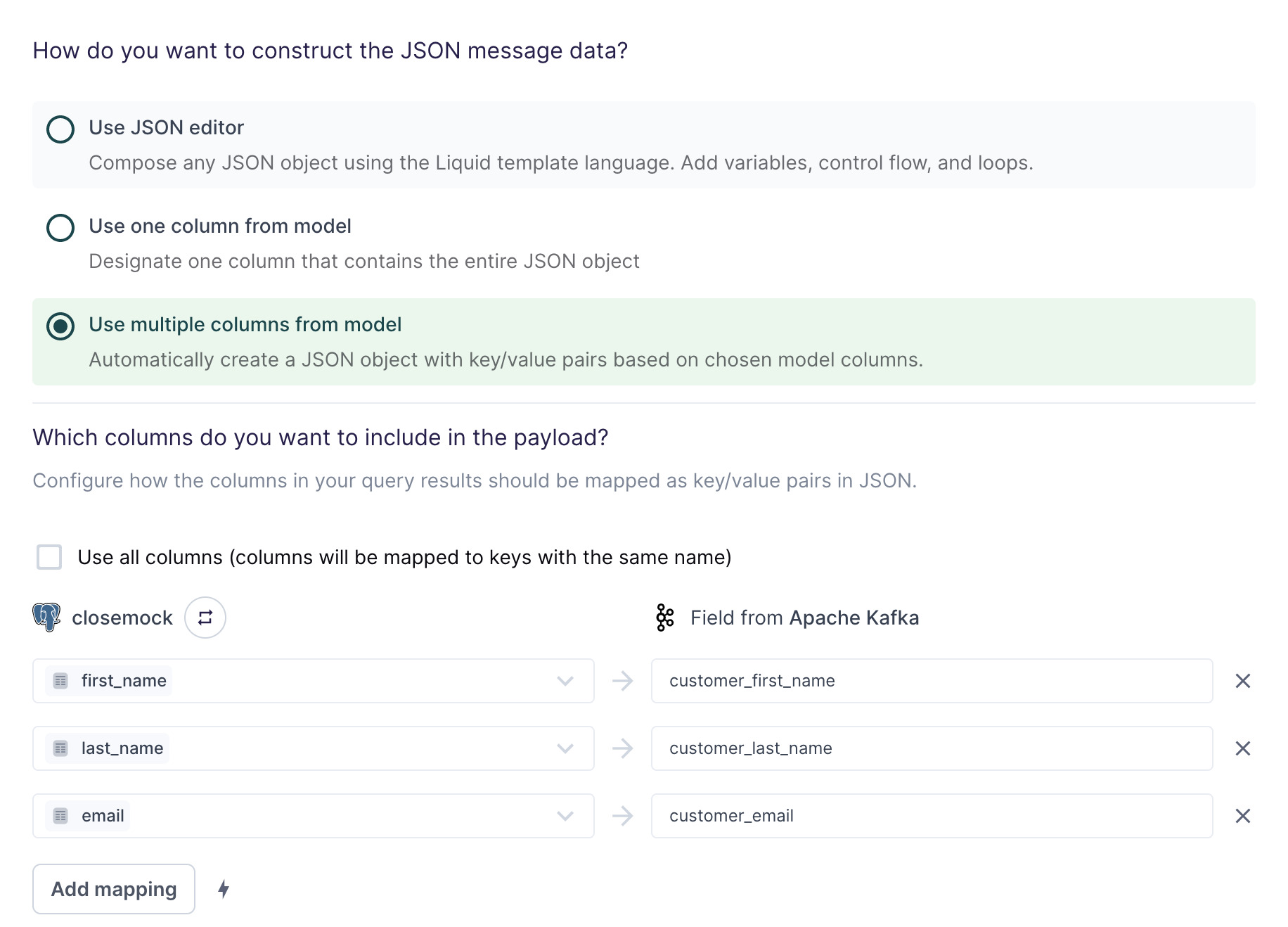
For the simplest use cases, Hightouch can construct a JSON object with key/value pairs based on multiple columns in your model.
Suppose your model looks like this:
| first_name | last_name | |
|---|---|---|
alice.doe@example.com | Alice | Doe |
bob.doe@example.com | Bob | Doe |
carol.doe@example.com | Carol | Doe |
The field mapping in the screenshot above would generate the following message data for the first row:
{
"customer_first_name": "Alice",
"customer_last_name": "Doe",
"customer_email": "alice.doe@example.com"
}
You can use the field mapper to rename fields. For example, first_name can
be mapped to customer_first_name.
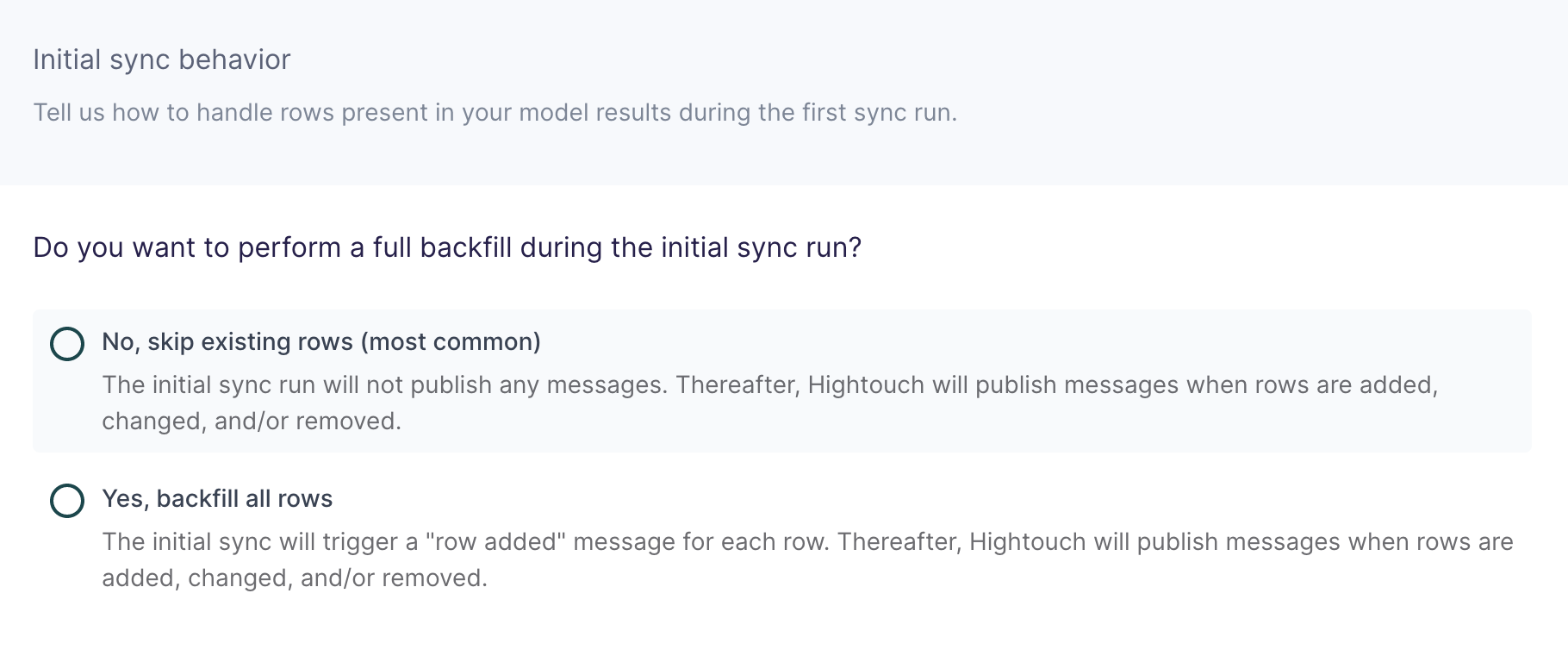
Configure initial sync behavior
In this step, you tell Hightouch how to handle rows present in your model results during the first sync run.
Certain workflows may require performing a backfill of all rows during the initial sync. For other use cases, you might only want to send messages in response to future data changes.
Tips and troubleshooting
Common errors
To date, our customers haven't experienced any errors while using this destination. If you run into any issues, please don't hesitate to . We're here to help.
Live debugger
Hightouch provides complete visibility into the API calls made during each of your sync runs. We recommend reading our article on debugging tips and tricks to learn more.
Sync alerts
Hightouch can alert you of sync issues via Slack, PagerDuty, SMS, or email. For details, please visit our article on alerting.
