| Audience | Marketers, Platform admins, Data and analytics engineers |
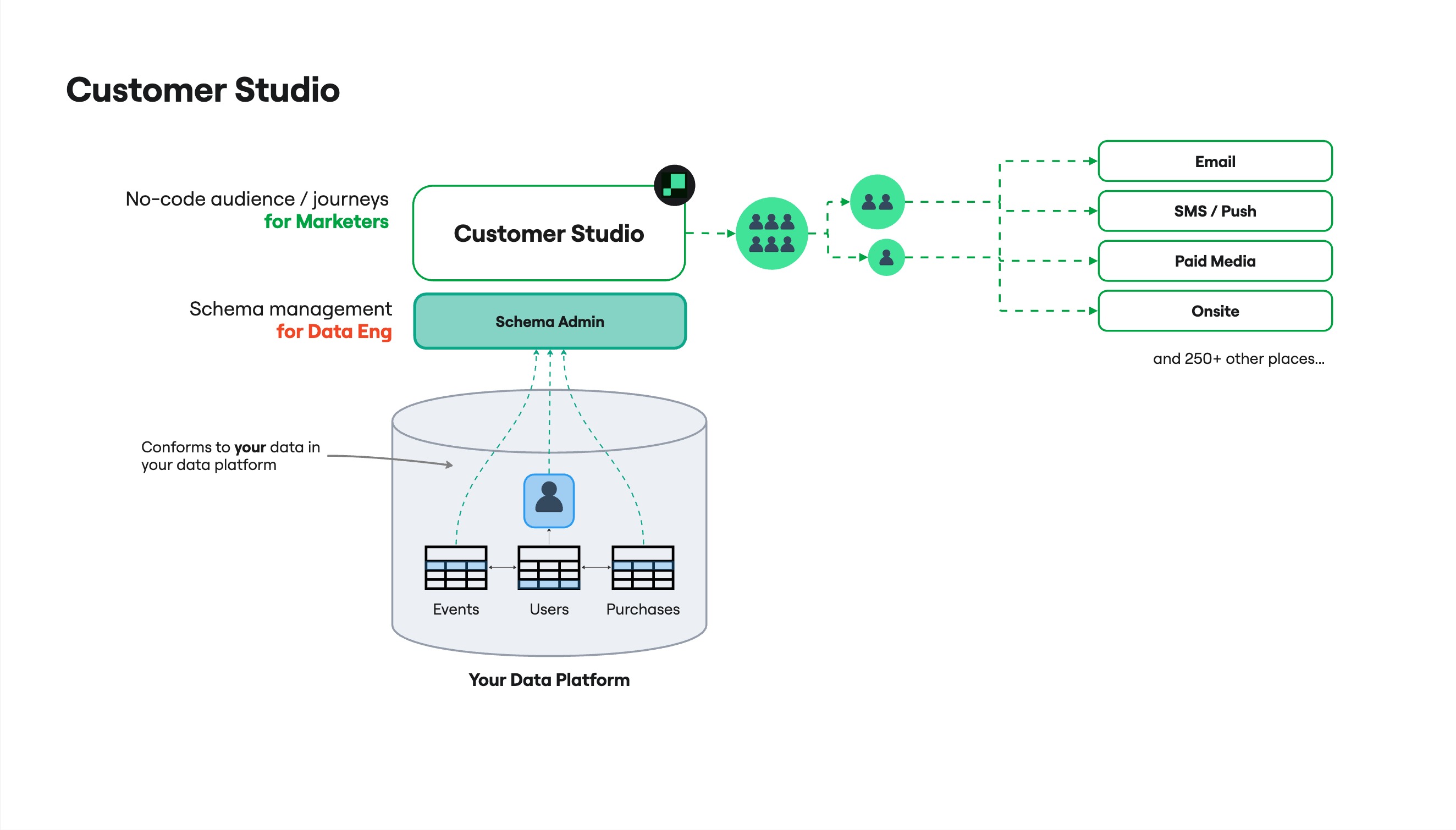
Customer Studio is a no-code audience builder where you define, activate, and manage audiences using data from your warehouse. It provides a visual interface for building audience logic and syncing users to tools like CRMs, ESPs, and ad platforms.
Customer Studio is available as an add-on to Business tier plans.
Learning objectives
After reading this article, you’ll understand:
- What Customer Studio is and how it fits into your workflow
- Who’s responsible for setup and day-to-day use
- Key features available in each stage of the workflow
- How to access Customer Studio in the Hightouch app
Overview
Customer Studio is a no-code audience builder for marketers. It allows you to define and manage customer audiences using your organization’s data, without writing SQL or relying on engineering support.
You can apply filters, traits, and real-time events to determine which users belong in an audience, then sync that audience to tools like ad platforms, CRMs, or email service providers (ESPs).
Because Customer Studio connects directly to your data warehouse, audiences remain current without manual list exports or updates. Data is not stored or copied unless explicitly configured.
Who uses it
| Role | Responsibilities | Learn more |
|---|---|---|
| Platform admins / Data teams | Set up sources and configure schema models, traits, and delivery controls | Setup instructions → |
| Marketers | Build, sync, and manage audiences for campaigns | How to use → |
Example: Target a high-value loyalty segment
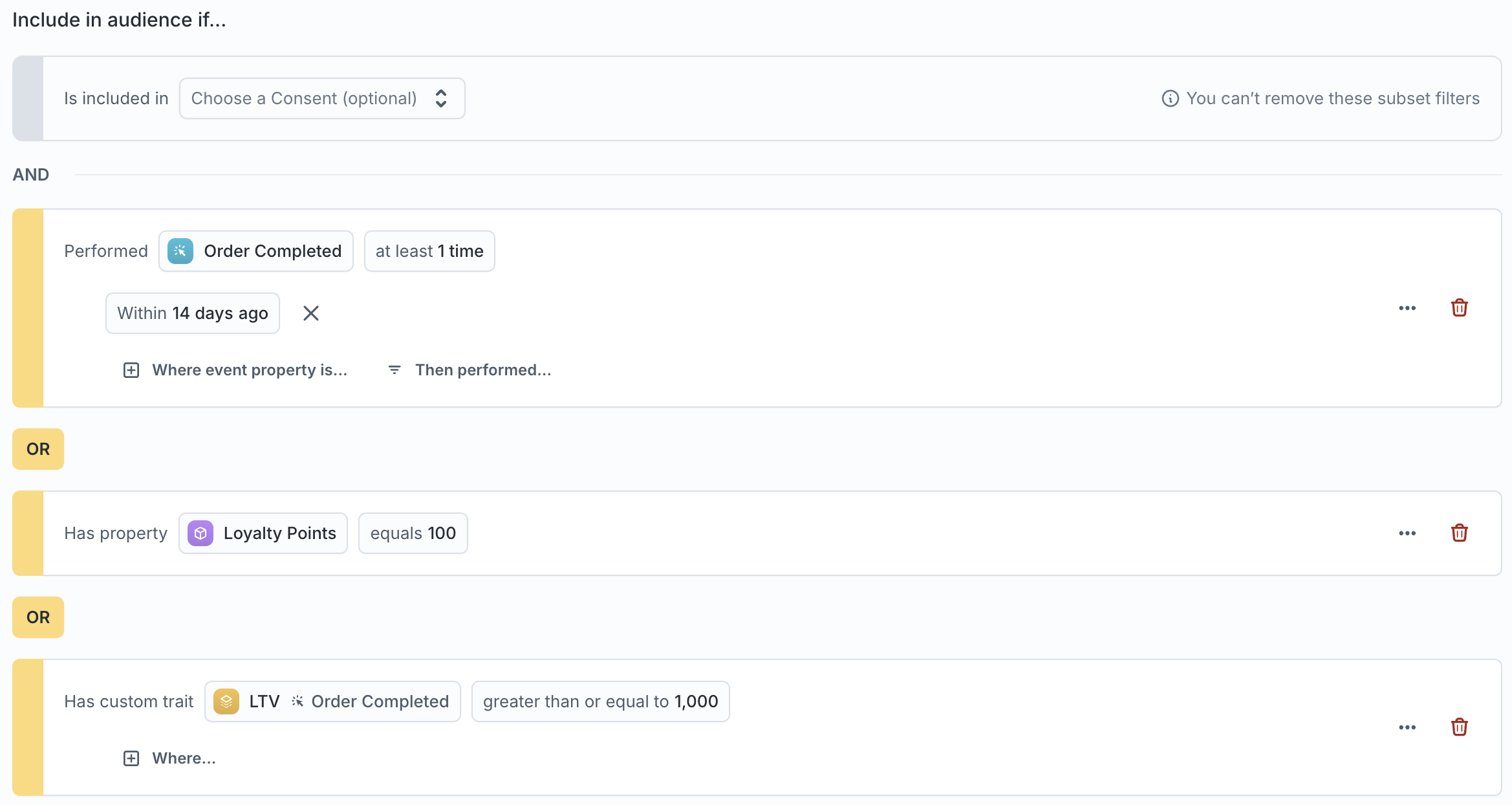
Let’s say you want to create a campaign for users who meet any of the following criteria:
-
Placed an order in the last 2 weeks
-
Are part of your loyalty program
-
Have a lifetime value over $1,000
You can define this logic using filters in the audience builder, combine them with AND/OR conditions, and preview the matching users before activating the audience.
Once saved, you can sync this audience to multiple tools—such as Klaviyo for email or Meta Ads for paid media—without rebuilding the segment in each platform.
Navigate to Customer Studio
To access Customer Studio in the Hightouch app:
-
Go to app.hightouch.com
-
In the left sidebar, click Customer Studio
Core workflow
The Customer Studio workflow is centered around three core steps: setting up your data schema, building audiences, and syncing them to destinations. These steps form the foundation for targeting and activation.
1. Set up your schema
Data teams connect relevant tables—such as users, purchases, product views, or support tickets—and define how these tables relate to each other. This creates the foundation that marketers use to filter, segment, and personalize audiences.
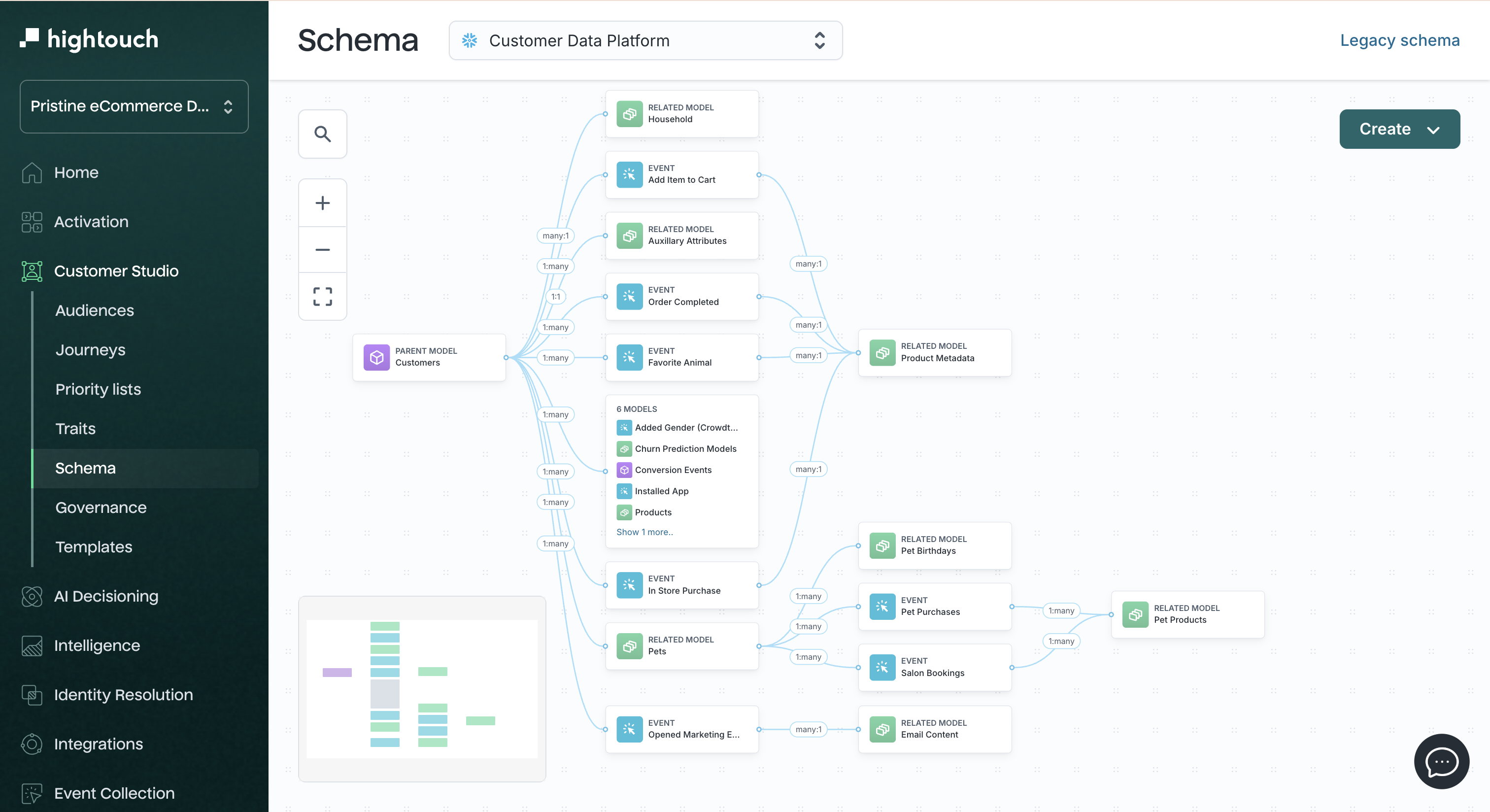
Before defining your schema, make sure at least one data source is connected to your Hightouch workspace.
2. Build your audience
Marketers use the visual audience builder to define which users should be included in a campaign. You can combine filters, traits, and event conditions—then preview audience size, inspect matching users, and fine-tune logic before syncing.
3. Sync to your tools
Once saved, marketers can sync audiences to destinations like CRMs, ad platforms, or email service providers. Choose a sync method that fits your use case:
-
Scheduled syncs for batch delivery (e.g., daily Meta Custom Audiences)
-
Real-time syncs for instant personalization (e.g., on-site or in-app experiences)
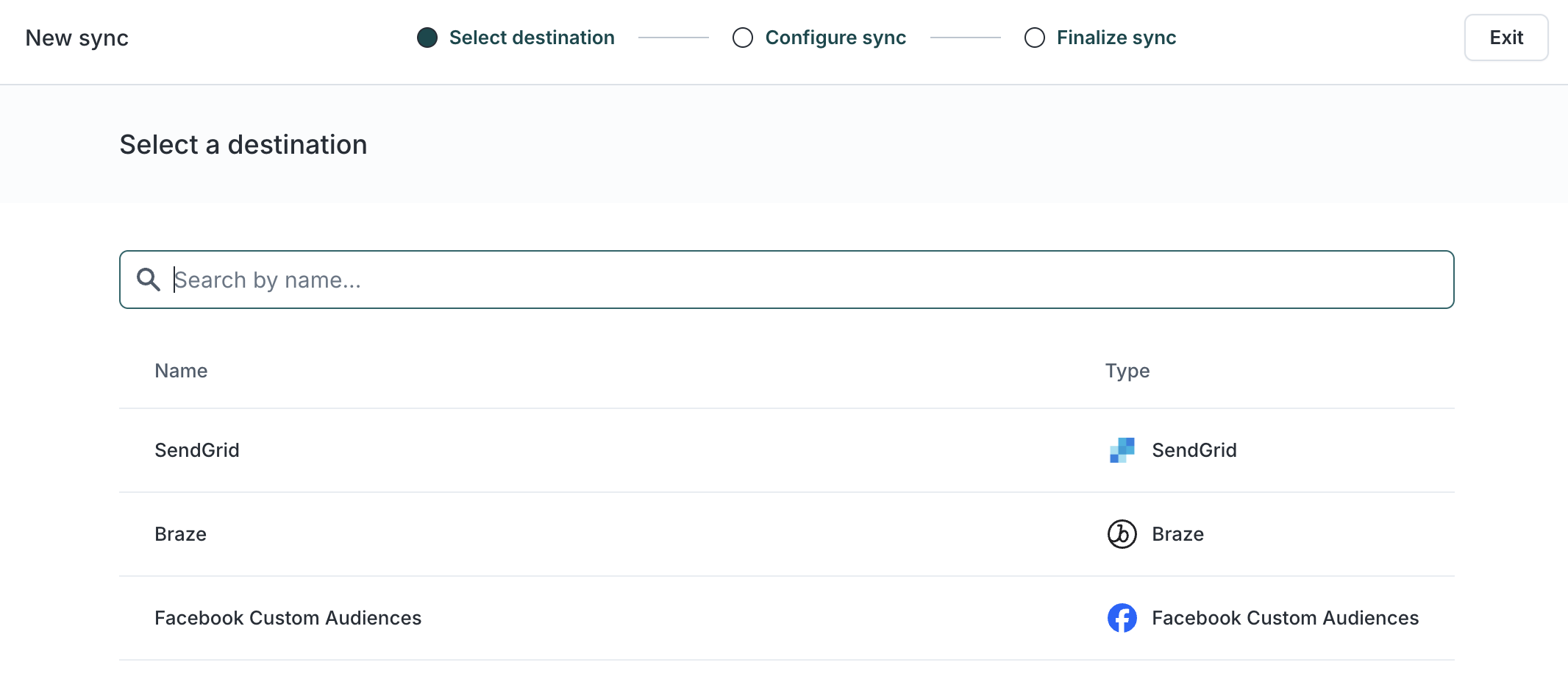
To sync your audience, at least one destination must be connected to your workspace.
Advanced personalization and management
After building and syncing your first audiences, you can layer on tools to support personalization, automation, testing, and compliance as needed.
Traits →
Custom calculated fields created by you and your data team. Traits allow you to use advanced logic—like scores, tiers, or rollups—in audience filters without writing code.
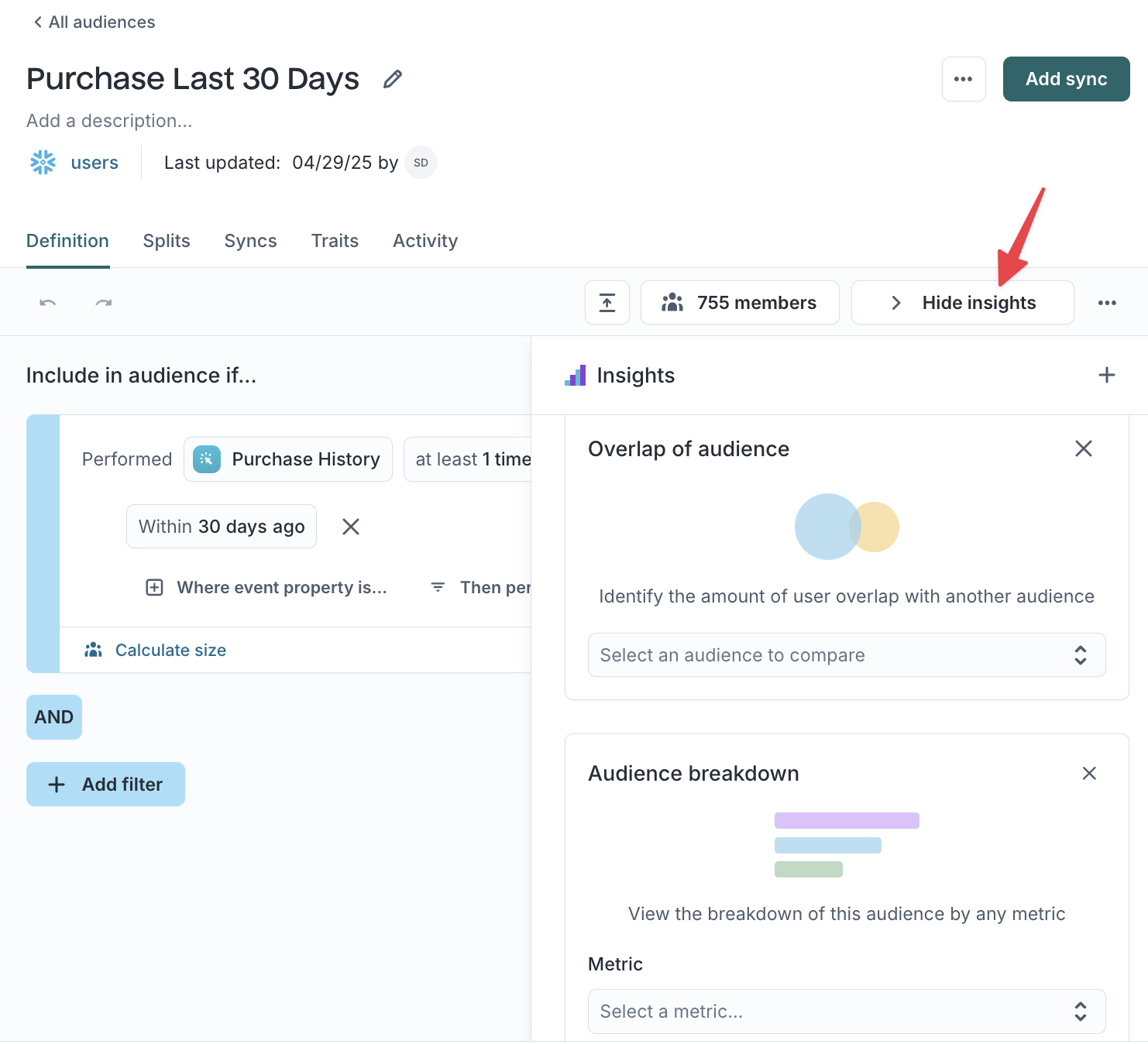
Insights →
A side panel that helps you analyze audience composition. Compare overlap with other audiences or break down members by attributes like geography or behavior.
Sampling →
A debugging and performance feature that limits audience previews to a small sample. Useful when working with large datasets or testing complex filters.
Templates →
Reusable audience logic that helps standardize targeting criteria across teams. Use templates to ensure consistency and speed up campaign setup.
Snapshots →
A point-in-time export of an audience’s membership. Snapshots preserve historical lists for compliance, measurement, or backfills—independent of sync timing.
Journeys →
A visual builder for multi-step campaign logic. Use journeys to trigger actions based on real-time user behavior, apply branching rules, and automate follow-ups.
Priority lists →
Tools for conflict resolution. Priority lists rank audiences so you can control which segment a user belongs to when they qualify for more than one.
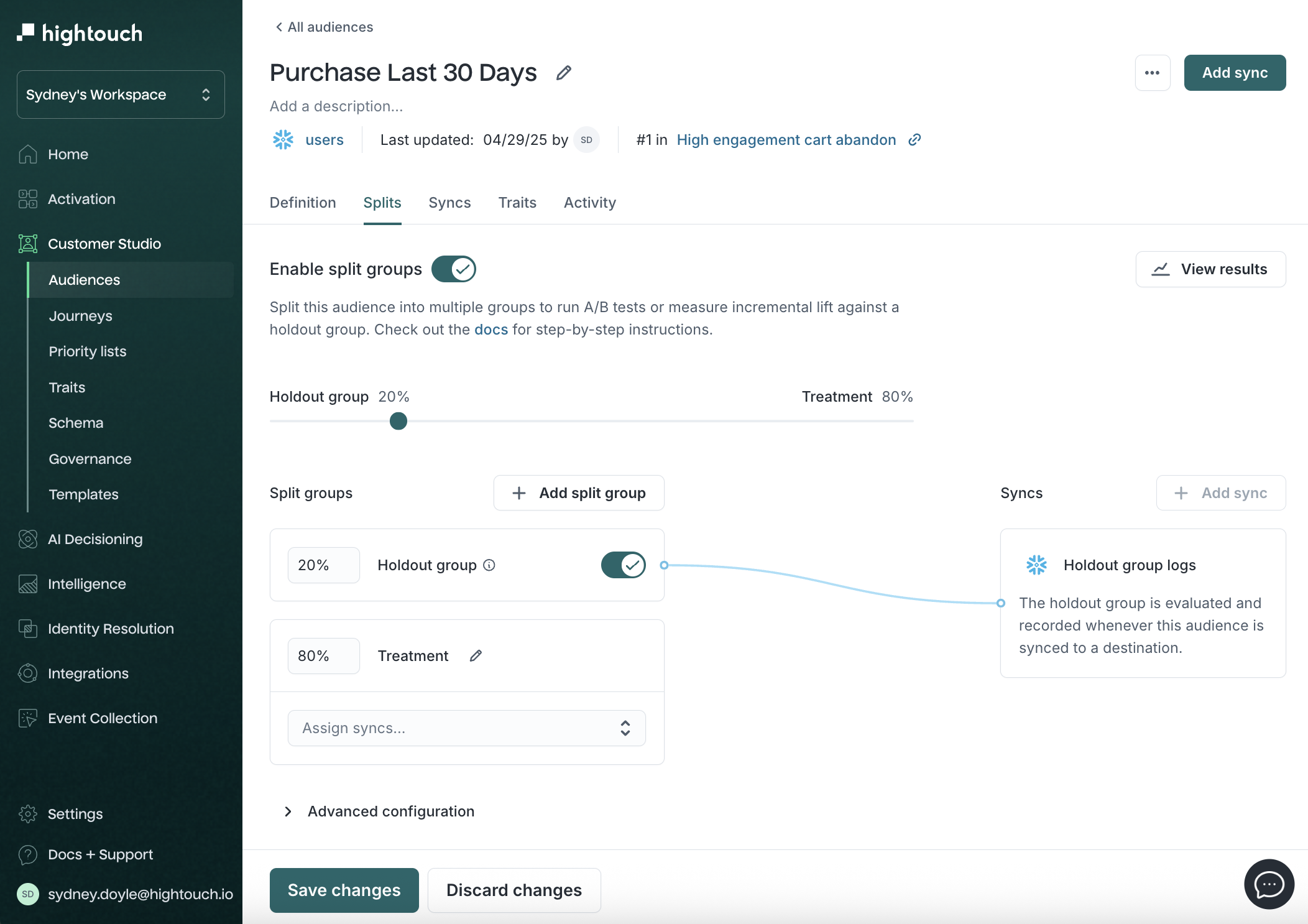
Splits →
Divide an audience into randomized groups to run A/B or multivariate tests. Useful for comparing different campaign treatments or creatives.
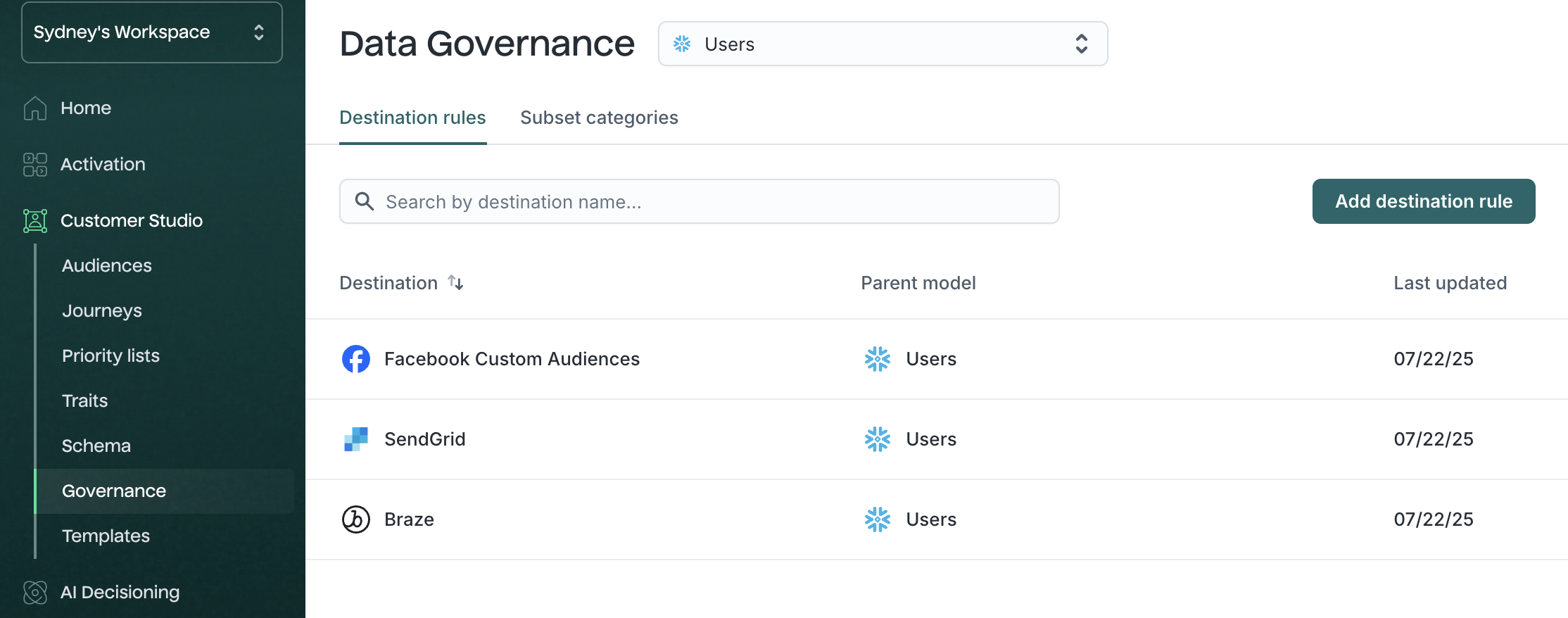
Destination rules →
Governance settings that apply conditions to when or how a destination receives data—for example, to prevent syncing users missing consent fields.
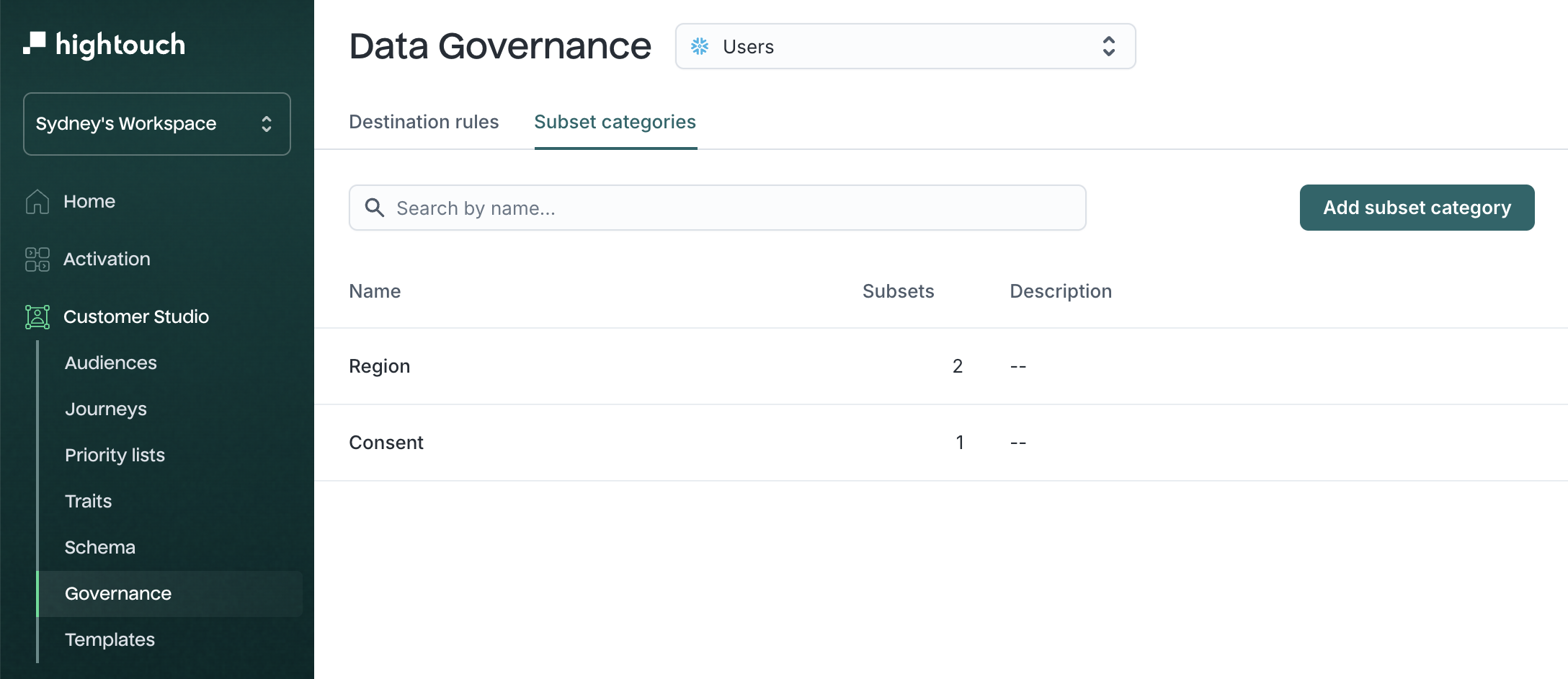
Subsets →
Reusable filters that scope which records can be synced to certain destinations. Useful for limiting syncs by region, subscription status, or compliance flags.
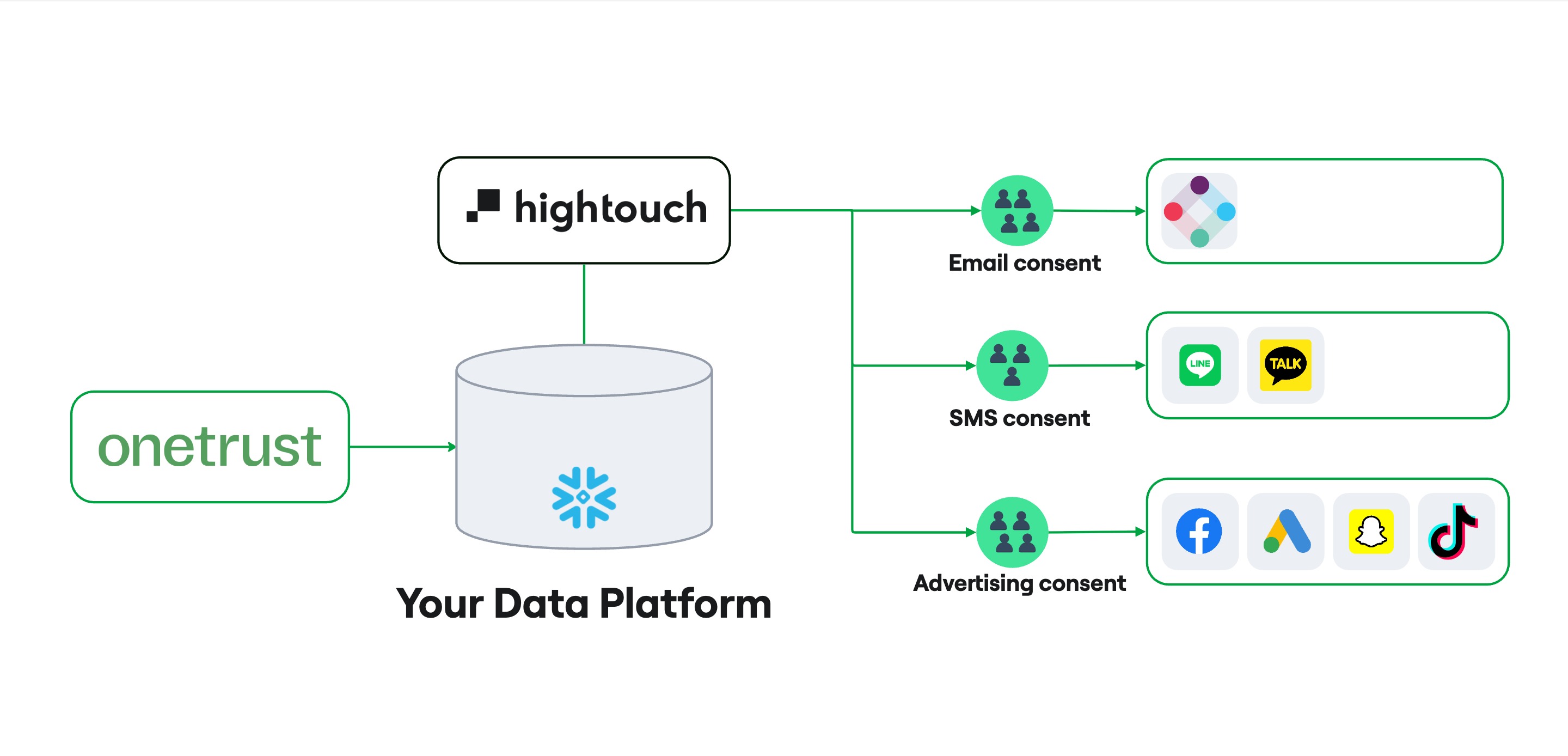
OneTrust Native Snowflake App →
Connects Hightouch to your OneTrust consent management platform to automatically exclude opted-out users from audience syncs.
Supported sources
Only the following sources support Customer Studio:
- Snowflake
- Databricks
- Google BigQuery
- Amazon Redshift*
- Amazon Athena
- Azure Synapse
- MS SQL Server
- PostgreSQL
- Greenplum
- Microsoft Fabric
* Customer Studio may not work with Amazon Redshift Spectrum due to its limitations around nested data. To mitigate these, you can try to query a materialized view during your parent model setup.