Hightouch provides label-based access control (LBAC) to provide granular access control to resources. Workspace owners can use label to:
- Enforce granular access control
- Enable cleaner workspace organization
- Unlock easier collaboration across teams and departments
What are labels?
Labels are structured as key/value pairs. For example, common keys include project, env, folder, and campaign. Values are attached to keys. Values for an env key could include dev, staging, and prod.
You can apply labels to any top-level resources, including sources, models, syncs, etc. Labels apply across all resources in the same workspace. For example, project labels applied to models can also be used for sources.
Add labels
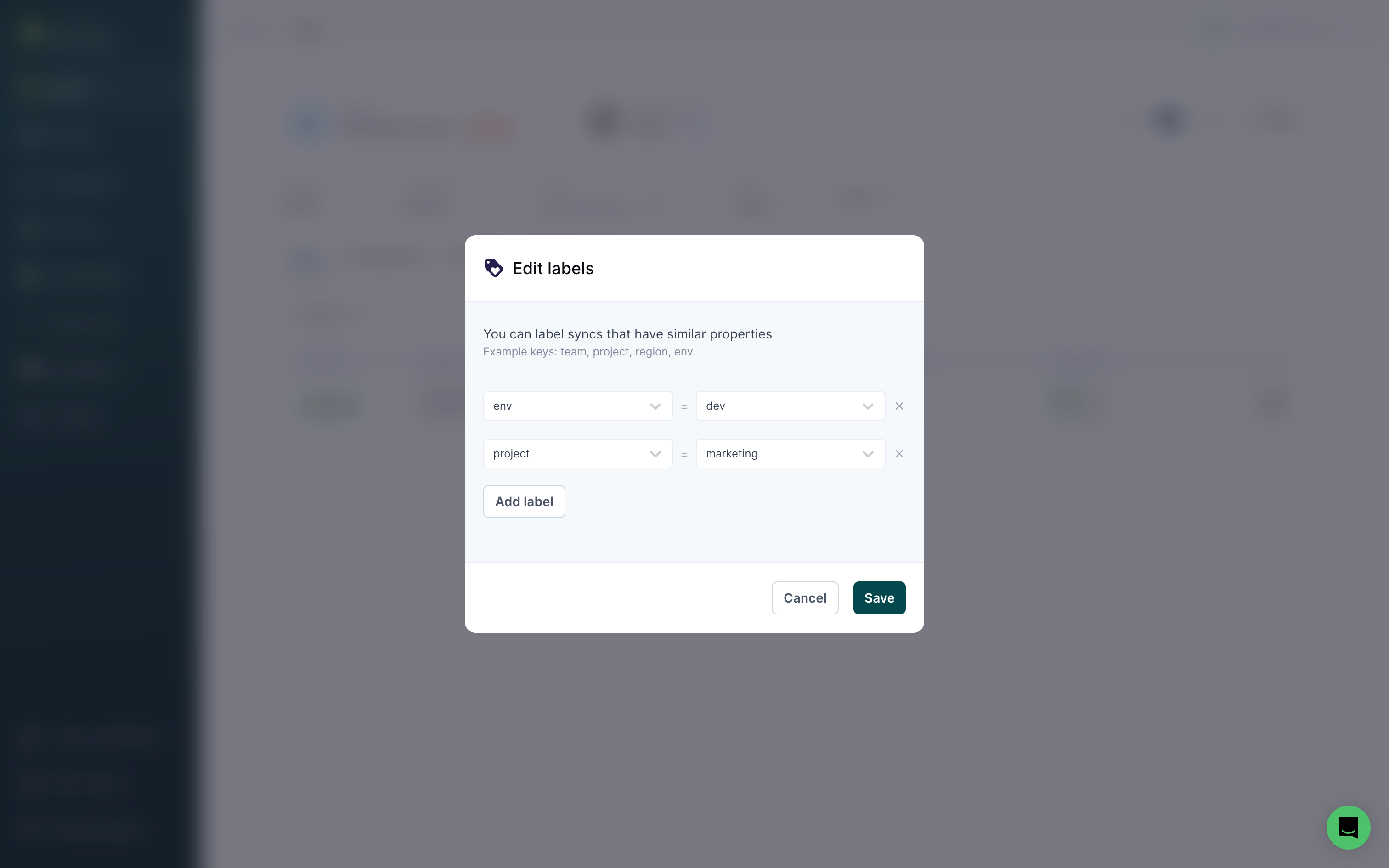
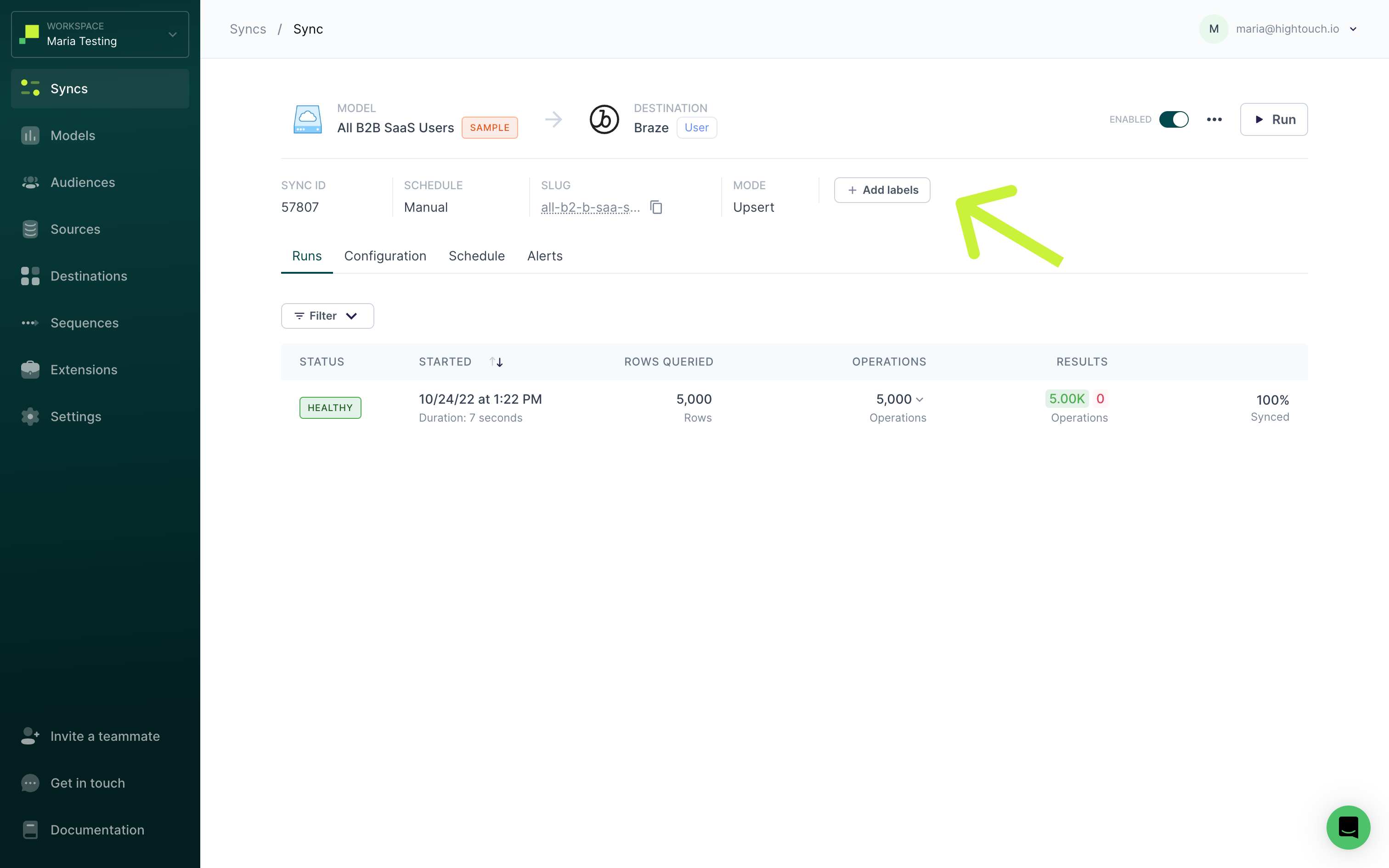
You can add labels to resources in Hightouch by going to any resource's overview page and clicking Add labels.
Then, enter one or more key/value pairs and click Save. Label names can include letters, numbers, spaces, underscores, and dashes.
Customer Studio only supports adding labels to audiences. Parent models, related models, and events don't support LBAC.
Filter by labels
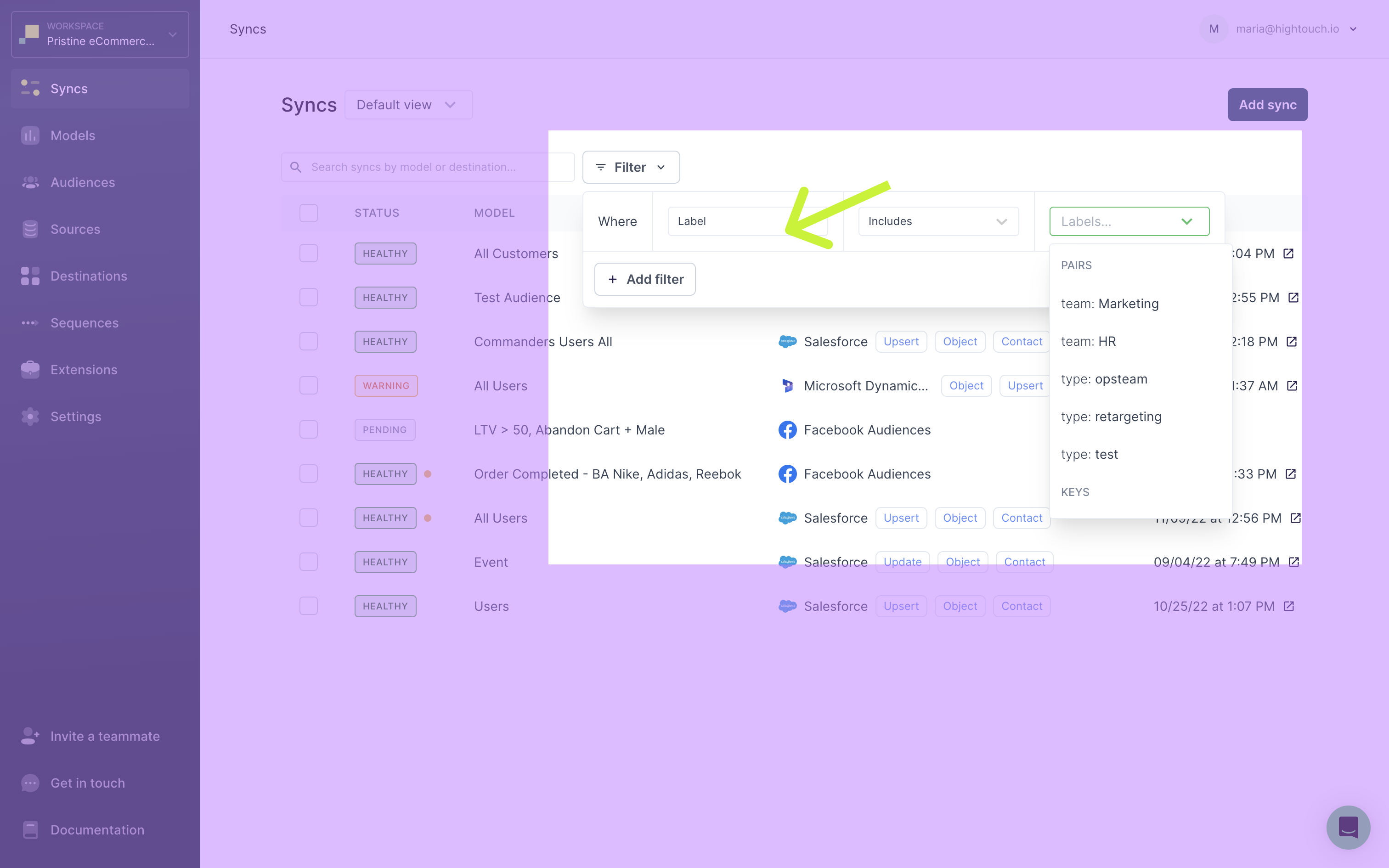
When viewing a top-level resource page, for example, the syncs page, you can select to Filter by labels, as well as other options like which user created the resource.
When filtering by label, you can filter all resources that include or exclude particular key/value pairs or keys.
Label-Based access control
You can restrict access to resources based on labels by creating custom roles. Label-based access is specified through a policy's conditions property. A policy is a JSON object defining the set of actions that users can take on resources. Read the role-based access control documentation to learn more about how a policy is structured.
{
"version": "2022-04-26",
"policies": [
{
"effect": "allow",
"actions": "read",
"resource": "model",
"conditions": {
"labels.team": {
"equals": "marketing"
}
}
}
]
}
What are conditions?
Conditions are nested objects consisting of:
- The resource the condition should apply to, either
source,models,destination, orlabels - A boolean statement evaluating the condition
Resources references
The following are resources you can reference in a condition:
| Header | Description |
|---|---|
source | References the source a sync is connected to |
model | References the model or audience a sync is connected to |
destination | References the destination a sync is connected to |
labels | References the label on the resource |
Resources are specified with dot notation: ${resource}.labels.${label-key}.
These are some examples of how you can specify resources in a condition:
source.labels.projectrefers to anyprojectlabels on sourcesmodel.labels.environmentrefers to anyenvironmentlabels on models or audiencesdestination.labels.teamrefers to anyteamlabels on destinationslabels.projectrefers to anyprojectlabels on any resources
As explained in the Add labels section, parent models, related models, and events don't support LBAC.
Boolean statements
Once you've specified a reference, you need to write a boolean statement to complete your condition. The boolean statement is also a key/value pair. The key is the boolean operator and the value is the operand.
Hightouch supports the following operators:
| Operator | Description | Applicable Resources |
|---|---|---|
in | Label is a member of an array | All |
notin | Label is not a member of an array | All |
equals | Label exactly matches pattern | All |
greaterthan | Label is greater than a value | All |
lessthan | Label is less than a value | All |
exists | Label refers to a resource that exists | All |
The following are some example boolean statements:
"equals": "marketing"evaluates whether the label matches"marketing""exists": trueevaluates whether the label exists"in": ["Marketing", "Sales"]evaluates whether the resource's labels matches any of the items in the array
Example label-based role
In this example, the Lifecycle Team Collaborator role has access to syncs that connect to destinations that have been the label team:lifecycle.
They can create syncs, but are only allowed read-access to destinations with the team:lifecycle label. Therefore, they can only access syncs connected to destinations with that label. Specifically, they can read, update, start, enable, and debug syncs connected to destinations with the team:lifecycle label. They have full-access to audiences.
{
"version": "2022-04-26",
"policies": [
{
"effect": "allow",
"actions": "create",
"resource": "sync"
},
{
"effect": "allow",
"actions": [
"read",
"update",
"start",
"enable",
"debugger"
],
"resource": [
"sync"
],
"conditions": {
"destination.labels.team": {
"equals": "lifecycle"
}
}
},
{
"effect": "allow",
"actions": "read",
"resource": [
"destination"
],
"conditions": {
"labels.team": {
"equals": "lifecycle"
}
}
},
{
"effect": "allow",
"actions": "*",
"resource": "audience"
}
]
}