When customer journeys span multiple devices, channels, and touchpoints, answering "What did my customer actually do?" becomes a complex challenge. A single person might click a mobile ad, browse on a tablet, and purchase on a desktop. Without stitching these actions together, marketers lose the ability to personalize experiences, measure effectively, and drive revenue.
Marketers don’t need more data, they need connected data. Identity resolution is how you solve fragmentation. By linking every action and attribute to a single customer, it becomes possible to personalize, measure, and grow with confidence.
What is Identity Resolution?
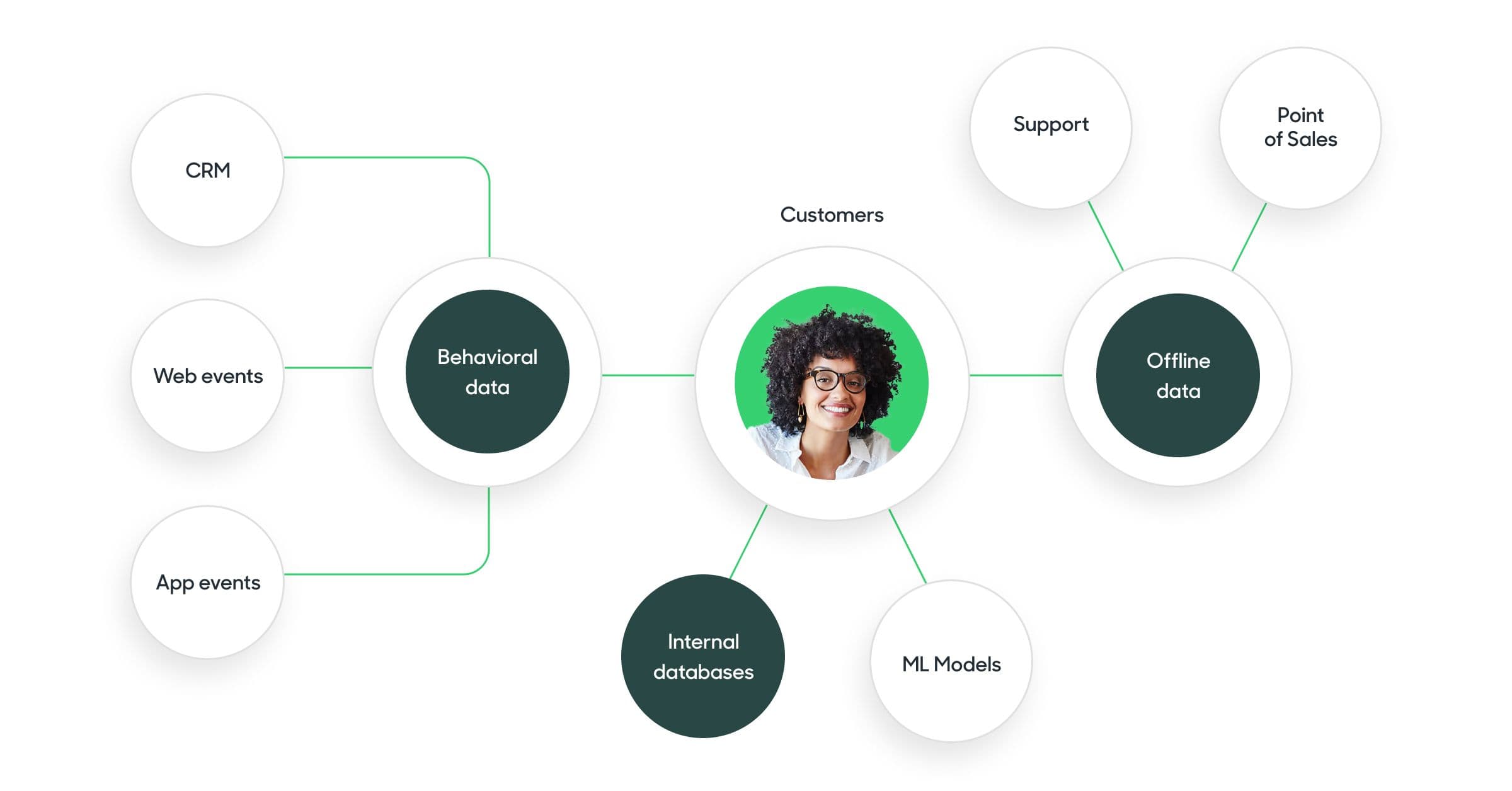
Identity resolution is the process of linking user actions and attributes across devices, touchpoints, and systems to build a unified customer profile. Its purpose is to consolidate online and offline data, so every behavior can be traced back to a known user or account.
This process often begins during data onboarding, where raw customer data from various sources, like web sessions, mobile apps, and in-store systems, is ingested and connected. Identity resolution ensures these fragmented identifiers are stitched into a single, actionable profile.
As customer journeys grow more complex, this becomes essential. With the average household owning 21 connected devices, it’s easy for a single customer to be represented by multiple disconnected profiles. That fragmentation leads to broken experiences, inaccurate ROI and churn measurement, and wasted marketing spend.
For example, a customer might browse your site on a desktop, see ads on Instagram via mobile, visit a retail store, and complete their purchase in your app. Identity resolution connects all these touchpoints, revealing the whole journey and enabling true personalization at scale.
What’s the Difference Between Identity Resolution and Entity Resolution?
Entity resolution is an umbrella term for stitching together disparate records that should all be aligned to a single profile. Identity resolution is an example of entity resolution, where the records that are stitched together are individual user records. Entity resolution can be used on other non-user records, such as accounts, to remove duplicate data and standardize records.
Entity resolution can help you look at customers in aggregate groups rather than as individual users. For example, a cable service may want to standardize all customer actions within household entities rather than individual users. The cable company is not selling to each discrete member of a household but instead to the entire household, and so rather than focusing on customer identity resolution, the cable company will work at a higher household level. Similarly, a company that sells software to other companies may care about identities at the account level rather than worrying about individual users from within a client's account.
We've written a separate article about entity resolution, but the fundamental approaches for identity resolution and entity resolution are similar.
How Does Identity Resolution Work?
Identity resolution begins by collecting identifiers from a user. These may include:
- Name
- Email address
- Phone number
- Device ID
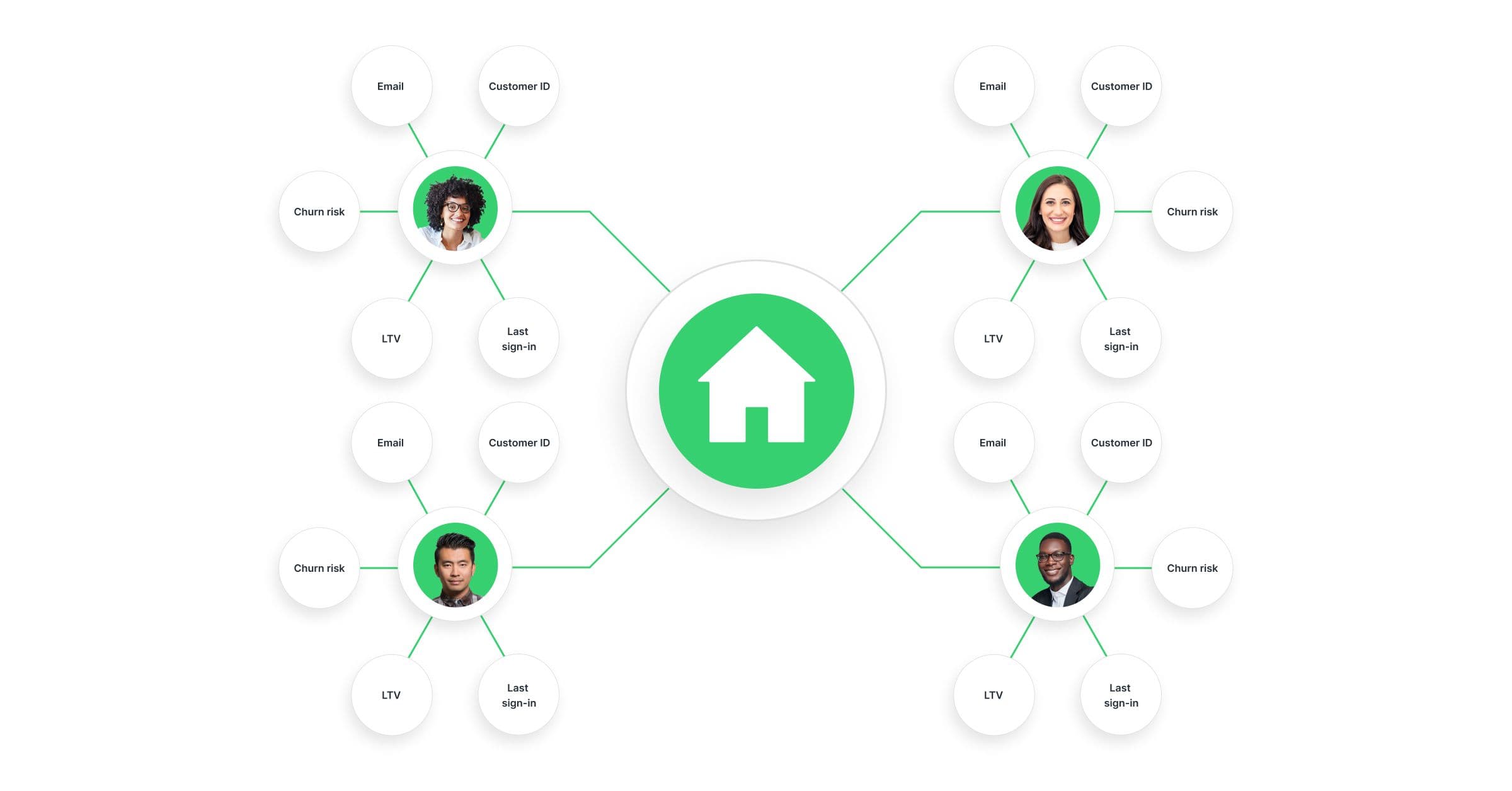
You store these identifiers in an identity graph, a centralized table that maps all attributes and identifiers associated with a customer across devices, platforms, and channels. Identity resolution rules and algorithms then connect these identifiers to form a single unified profile per user. Your identity graph updates continuously as new identifiers come in, maintaining a persistent ID for each customer.
Persistent IDs are critical because they provide a stable way to recognize the same customer across systems, even when individual identifiers (like email or device ID) change. This enables accurate personalization, consistent customer experiences, improved measurement, and better compliance with privacy regulations by allowing controlled management of customer data.
Why Does Identity Resolution Matter?
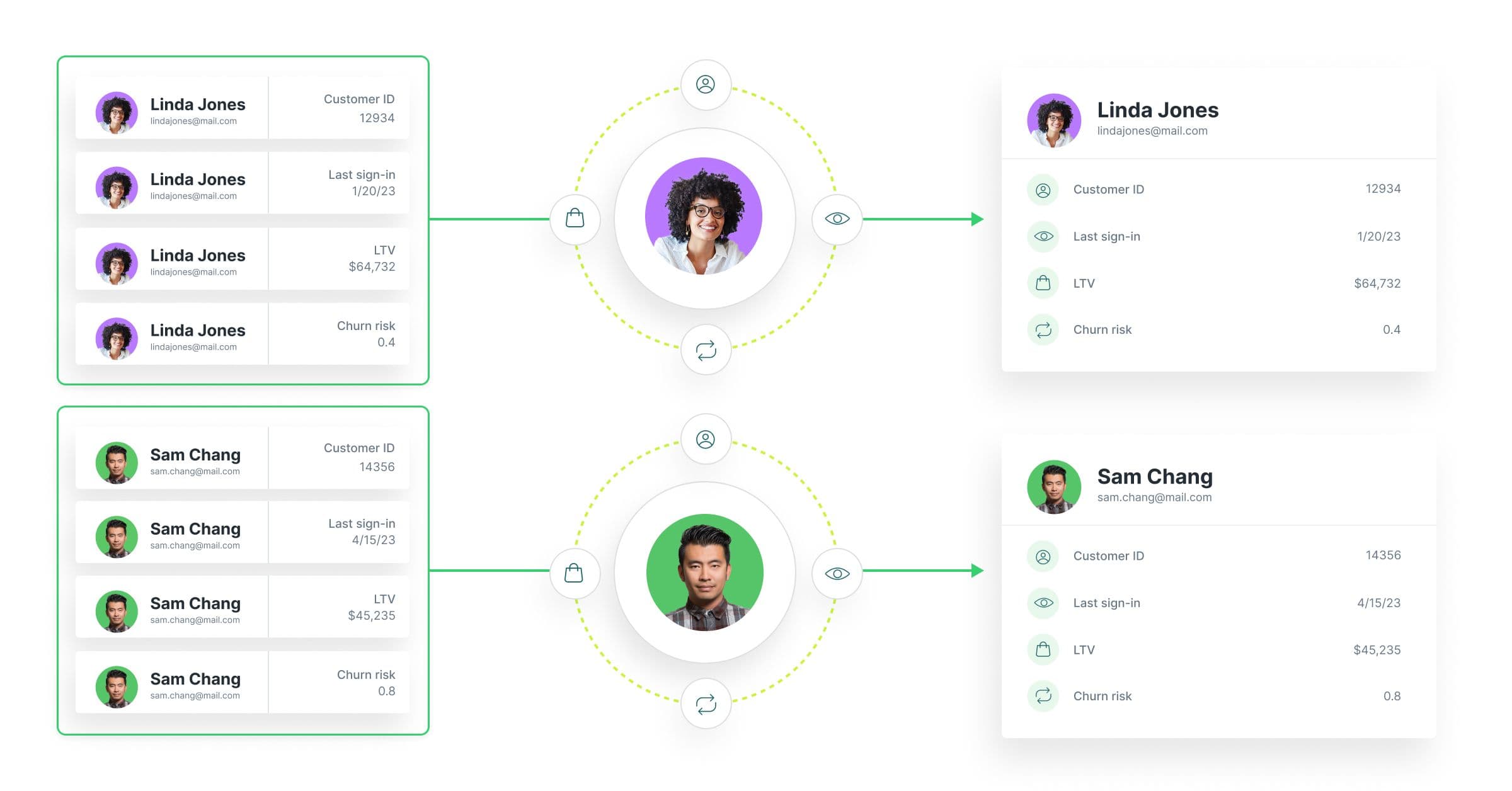
Without identity resolution, marketers are essentially flying blind. When customer data is scattered across systems and tied to disconnected identifiers, you lose sight of who your customers really are. One person might show up in your database as five separate profiles: one from an email sign-up, one from mobile app activity, one from an in-store purchase, and so on. Without a way to reconcile those identities, you’re left with a fractured view that leads to poor decisions and a broken customer experience.
This fragmentation creates real problems. You end up targeting the same person multiple times across channels with the same message or irrelevant promotions, which not only wastes ad spend but can actively damage trust. You’re promoting products they already bought, sending emails they’ve opted out of, or showing ads that don’t reflect where they are in their journey. Identity resolution solves this by deduplicating profiles, giving you a single, unified view of each customer so your outreach is accurate, relevant, and timely.
It also unlocks deeper behavioral insights. When every action is tied back to a known profile, you can finally understand what your customers are doing across touchpoints. That means better personalization, more intelligent segmentation, and more accurate attribution. Instead of guessing which channels drove a conversion, you can see the path from first touch to final purchase.
Just as critically, identity resolution plays a vital role in privacy and compliance. Centralizing consent preferences and honoring opt-out requests across all systems helps ensure you respect customer choices and meet legal obligations. Without it, you risk sending messages that violate user preferences or even compliance regulations, simply because one part of your stack didn’t know what the other was doing.
In short, identity resolution isn’t just a nice-to-have, it’s the foundation for building trusted, data-driven customer relationships that perform.
What's the difference between deterministic matching and probabilistic matching?
There are two primary methods of identity resolution: deterministic matching and probabilistic matching.
Deterministic matching relies on exact, verified data points, such as email addresses, phone numbers, or user IDs, to connect profiles with certainty. For example, if a user logs in on mobile using their email and later logs in on desktop with the same email, you can confidently merge these interactions into a single profile. Because it uses known identifiers, deterministic matching offers a high degree of accuracy and is commonly used when first-party data is available.
Probabilistic matching uses algorithms and statistical models to infer relationships between identifiers. It analyzes patterns such as IP addresses, device types, and behavioral signals to estimate the likelihood that two profiles belong to the same person. For instance, if one profile uses j.smith@ and another uses john.smith@, the system may infer these represent the same user and merge them. While less precise than deterministic methods, probabilistic matching is more scalable and flexible, especially useful when deterministic data is unavailable.
The key difference between deterministic and probabilistic matching is that deterministic matching uses known identifiers to link profiles with certainty, while probabilistic matching uses patterns and probabilities to make educated guesses about identity.
Realistically, a sophisticated business should be leveraging both forms of identity resolution in different use cases. For highly personalized messages, the accuracy of deterministic identity resolution is essential for success. For broader goals like building audiences in advertising platforms, the greater power of probabilistic identity resolution will lead to more impactful campaigns, even if some individual customers are incorrectly linked to actions others have taken. Ultimately, different business units should rely on different identity resolution models depending on their needs for fidelity and reach.
Hightouch’s Adaptive Identity Resolution allows you to toggle between different confidence levels– and determinstic and probabilistic methods– for different use cases. That way, you can tailor your identity resolution strategy for each use case, all from the same identity graph in your data warehouse.
The mechanics of warehouse identity resolution and how CDPs differ
Not all identity resolution is created equal. While many Customer Data Platforms (CDPs) offer identity resolution as a built-in feature, the underlying architecture matters, and it dramatically impacts the accuracy, flexibility, and usefulness of your customer profiles.
With warehouse-native identity resolution, everything runs directly on your first-party data in your warehouse. That means:
- You own the identity graph
- You have access to every touchpoint and dataset already in your warehouse
- You can customize matching logic to fit your specific use cases
- There’s no black box, everything is transparent and configurable
By contrast, CDP-based identity resolution typically requires you to copy data out of your warehouse into a separate system. You’re locked into predefined matching logic, often without visibility into how profiles are merged. The identity graph lives inside the CDP, not your infrastructure, and that limits your ability to control, audit, or extend the data powering your customer experiences.
Warehouse-native identity resolution is foundational for companies embracing the composable CDP model. It gives you flexibility and ownership without sacrificing ease of use. Hightouch even goes a step further, supporting both deterministic and probabilistic resolution from the same setup, so you can apply high-accuracy matching for transactional use cases and higher-reach matching for paid media campaigns, all from the same unified platform.
If your goal is to maximize trust, scale, and activation across all your data, warehouse-native identity resolution is the clear path forward.
Identity resolution use cases
Identity resolution allows you to unify fragmented customer data across devices and touchpoints. This enables more personalized, efficient, and insight-driven marketing. Below are key use cases that show how identity resolution improves engagement, targeting, and analytics:
- Deliver more accurate product recommendations: When all customer identifiers are connected and their behavior is understood across devices and channels, you gain a complete picture of each user. This holistic view allows you to recommend products that truly align with individual interests, which improves conversion rates and drives more meaningful engagement.
- Enable cross-channel targeting: Identity resolution helps you recognize the same user across devices. This means you can retarget users across channels without duplication or missed opportunities. For instance, if a user abandons a cart on desktop, you can send a personalized push notification to their mobile device to complete the purchase.
- Improve suppression and reduce waste: With a unified customer view, you can suppress users who have already converted, preventing unnecessary ad spend and message fatigue. For example, pixel-based remarketing might mistakenly target existing subscribers who appear anonymous due to device or browser changes. Identity resolution corrects for this by enabling suppression across email, SMS, in-app, and paid social, helping protect the customer experience and ensure efficient budget allocation.
- Connect online and offline experiences: Identity resolution bridges the gap between in-store and online activity. You can match offline purchases to online profiles, enabling more informed marketing strategies. For example, if a customer browses online but typically shops in-store, you might mail a physical coupon rather than send another email.
- Enhance cross-device analytics: By linking user sessions and actions across devices and channels, identity resolution provides a more comprehensive view of the customer journey. This leads to deeper behavioral insights and smarter, faster decision-making.
- Ensure compliance and respect privacy preferences: Identity resolution allows you to honor user consent and opt-out preferences across systems. When a customer unsubscribes or opts out in one channel, you can ensure that choice is enforced everywhere, email, ads, push, and more. This centralized visibility helps reduce compliance risk, maintain trust, and uphold data regulations.
How different industries use identity resolution
While the fundamentals of identity resolution stay the same, the why behind it varies across industries. From fraud prevention in finance to cross-channel targeting in retail, identity resolution unlocks different kinds of value depending on the customer journey, data complexity, and personalization goals of each sector. Here’s how leading industries are putting it to work:
Retail and e-commerce
In retail, customers rarely buy in a straight line. They might browse on mobile, price check on desktop, visit a store, and complete their order later in an app. Without identity resolution, all of those actions live in silos, and the retailer is stuck guessing.
By stitching these interactions into a unified profile, retailers can deliver truly personalized product recommendations, offer smarter discounts based on purchase history, and re-engage cart abandoners with the right message on the right device. Identity resolution also fuels loyalty programs by connecting offline purchases with digital behavior, so marketers can reward the whole journey, not just the final click.
Financial services
In banking, customers might have checking accounts, credit cards, investment portfolios, and loans, often spread across different internal systems. That fragmentation makes it hard to deliver relevant financial advice, or worse, can blind the institution to signs of fraud.
Identity resolution brings all these data sources together to create a secure, compliant, 360-degree view of the customer. This allows financial institutions to proactively surface better product recommendations, detect anomalies across channels, and streamline KYC (Know Your Customer) processes, all while precisely honoring opt-out preferences and consent requirements.
Healthcare
Patients often see multiple providers, use different insurance plans, and move between in-person visits and telehealth. Their data is scattered across EMRs, billing systems, and intake forms, making it hard to deliver consistent care.
Identity resolution helps healthcare organizations merge these fragmented records into a single, accurate patient profile. This enables better diagnosis, fewer redundant tests, and smoother provider care transitions. It also ensures that patient privacy preferences and consent directives are enforced everywhere their data lives.
Media and entertainment
In the streaming era, media companies need to know who’s watching, not just what’s being watched. However, when a single viewer uses multiple devices, profiles can become fragmented, and personalization breaks down.
Identity resolution connects the dots between mobile apps, smart TVs, websites, and OTT platforms, enabling more precise ad targeting, tailored content recommendations, and better insight into viewer preferences. It also allows platforms to attribute subscriptions and engagement to actual users, not just anonymous device IDs.
Travel and hospitality
A traveler might research flights on their phone, book a hotel on a desktop, check in at a kiosk, and message support in-app. Each action is isolated without identity resolution, leading to missed upsell opportunities and disconnected service.
By building a unified traveler profile, hospitality brands can offer relevant add-ons (like airport transfers or room upgrades), personalize loyalty experiences, and empower service teams with context on every interaction. Identity resolution supports smoother communication across pre-trip, in-trip, and post-trip touchpoints.
B2B and SaaS
B2B buying decisions rarely come from a single person. They involve teams, long sales cycles, and multiple digital and human touchpoints. But with data siloed between product analytics, CRMs, and marketing platforms, it's hard to know who’s engaging, or how.
Identity resolution links user-level behavior (like feature adoption or support tickets) to the right account and stakeholders. This empowers sales and marketing teams to personalize outreach, score leads more accurately, and run smarter account-based campaigns. It also unifies reporting across lifecycle stages, helping teams understand what drives conversions and retention.
How to implement identity resolution?
Identity resolution requires a methodical, scalable approach that balances technical execution, data quality, privacy compliance, and future growth. Here are the key phases to guide a successful rollout:
1. Audit your existing data
Begin with a comprehensive audit of the customer data collected across systems and touchpoints. Identify available identifiers, such as emails, phone numbers, device IDs, and customer IDs, and assess data quality. Look for gaps, duplicates, outdated records, or inconsistencies. Understanding your current data foundation is essential before building identity resolution logic.
2.Confirm consent and compliance
Before linking or activating customer data, make sure you’ve collected consent. Align with privacy regulations like GDPR, CCPA, and any industry-specific standards. Establish data governance policies to manage access, enforce usage rules, and uphold customer rights across systems.
3. Centralize and normalize data
Identity resolution performs best on centralized, standardized data. Consolidate customer data from fragmented sources into a single repository, such as a data warehouse or lake. Normalize field formats, clean inconsistencies, and structure records to support accurate matching. If your data is messy, your identity resolution will be too. Clean, well-structured data is what makes reliable identity resolution possible.
4. Define your matching strategy
Determine how customer records will be linked. To ensure precision, use deterministic matching for exact identifiers like emails or customer IDs. Apply probabilistic methods, based on inferred signals like IP addresses or device patterns, for anonymous or partial data. Many teams adopt a hybrid approach to balance match rate with accuracy.
5. Choose your implementation model
Select an approach that fits your team’s resources and infrastructure:
- Build In-House: Develop custom matching logic using SQL or other tools within your existing data stack.
- Use a CDP: Leverage Customer Data Platforms with built-in identity resolution features.
- Go Warehouse-Native: Deploy tools that run directly within your cloud data warehouse for better control and scalability.
- Work with a Specialist: Partner with vendors focused exclusively on identity resolution for advanced use cases and dedicated support.
What tools help with identity resolution?
Several modern tools support identity resolution by enabling flexible, accurate matching of customer records directly within your data infrastructure. Below are three leading options that differ in approach, flexibility, and integration:
- Hightouch’s Adaptive Identity Resolution is a warehouse-native identity resolution solution that runs directly on your first-party data. Your identity graph lives in your data warehouse, so you fully own it and have access to every customer touchpoint and attribute. You can define precise deterministic and probabilistic matching rules, build multiple graphs for different use cases, and customize everything to fit your business, no black boxes, no data duplication. Unlike traditional CDPs, Hightouch gives you complete control, transparency, and flexibility, all without moving data out of your stack.
- Zingg is an open-source identity resolution tool that runs natively on platforms like Snowflake and Databricks. It uses machine learning to unify and deduplicate customer records, with configurable matching rules and entity resolution logic. Zingg’s open-source framework gives data teams the flexibility to build and customize workflows within their existing infrastructure. It’s a strong choice for teams seeking scalable, warehouse-native identity resolution with full control and transparency.
- Truelty helps you specifically for identity resolution in Snowflake, offering a streamlined way to deduplicate and unify customer data without exporting it to external systems. Optimized for Snowflake’s architecture, Truelty enables users to define rules for handling data inconsistencies and fragmented identities at scale. The result is a cleaner, more accurate customer view, delivered natively within your data environment.
Closing thoughts
Identity resolution isn’t just a backend process, it’s the foundation for delivering the relevant, real-time experiences your customers expect. Without it, your messaging is fragmented, your touchpoints are disconnected, and your customer insights are incomplete.
To get it right, identity resolution needs to run where your data lives: the warehouse. That’s what makes Hightouch different. As a warehouse-native solution, Hightouch gives you full ownership of your identity graph, complete access to every piece of customer data, and the flexibility to define matching logic that fits your needs.
With support for deterministic and probabilistic methods, you can build unified profiles that are accurate, configurable, and ready to activate across your entire marketing stack.
Want to see how it works? Book a demo and discover how Hightouch can help you unlock true personalization at scale.
















